Page 242 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 242
Introduction to Acid-Base Disorders 233
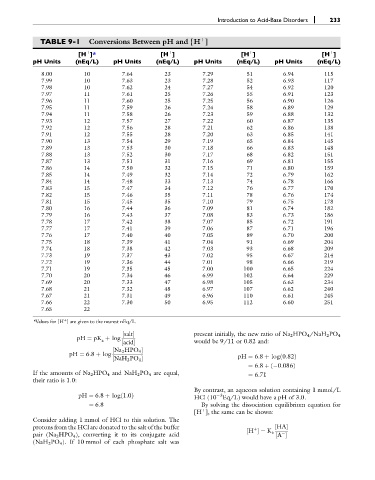
TABLE 9-1 Conversions Between pH and [H ]
þ
[H ]* [H ] [H ] [H ]
þ
þ
þ
þ
pH Units (nEq/L) pH Units (nEq/L) pH Units (nEq/L) pH Units (nEq/L)
8.00 10 7.64 23 7.29 51 6.94 115
7.99 10 7.63 23 7.28 52 6.93 117
7.98 10 7.62 24 7.27 54 6.92 120
7.97 11 7.61 25 7.26 55 6.91 123
7.96 11 7.60 25 7.25 56 6.90 126
7.95 11 7.59 26 7.24 58 6.89 129
7.94 11 7.58 26 7.23 59 6.88 132
7.93 12 7.57 27 7.22 60 6.87 135
7.92 12 7.56 28 7.21 62 6.86 138
7.91 12 7.55 28 7.20 63 6.85 141
7.90 13 7.54 29 7.19 65 6.84 145
7.89 13 7.53 30 7.18 66 6.83 148
7.88 13 7.52 30 7.17 68 6.82 151
7.87 13 7.51 31 7.16 69 6.81 155
7.86 14 7.50 32 7.15 71 6.80 159
7.85 14 7.49 32 7.14 72 6.79 162
7.84 14 7.48 33 7.13 74 6.78 166
7.83 15 7.47 34 7.12 76 6.77 170
7.82 15 7.46 35 7.11 78 6.76 174
7.81 15 7.45 35 7.10 79 6.75 178
7.80 16 7.44 36 7.09 81 6.74 182
7.79 16 7.43 37 7.08 83 6.73 186
7.78 17 7.42 38 7.07 85 6.72 191
7.77 17 7.41 39 7.06 87 6.71 196
7.76 17 7.40 40 7.05 89 6.70 200
7.75 18 7.39 41 7.04 91 6.69 204
7.74 18 7.38 42 7.03 93 6.68 209
7.73 19 7.37 43 7.02 95 6.67 214
7.72 19 7.36 44 7.01 98 6.66 219
7.71 19 7.35 45 7.00 100 6.65 224
7.70 20 7.34 46 6.99 102 6.64 229
7.69 20 7.33 47 6.98 105 6.63 234
7.68 21 7.32 48 6.97 107 6.62 240
7.67 21 7.31 49 6.96 110 6.61 245
7.66 22 7.30 50 6.95 112 6.60 251
7.65 22
*Values for [H ] are given to the nearest nEq/L.
þ
½salt present initially, the new ratio of Na 2 HPO 4 /NaH 2 PO 4
pH ¼ pK þ log
a
½acid would be 9/11 or 0.82 and:
½Na 2 HPO 4
pH ¼ 6:8 þ log
ð
½NaH 2 PO 4 pH ¼ 6:8 þ log 0:82Þ
¼ 6:8 þð 0:086Þ
If the amounts of Na 2 HPO 4 and NaH 2 PO 4 are equal, ¼ 6:71
their ratio is 1.0:
By contrast, an aqueous solution containing 1 mmol/L
ð
pH ¼ 6:8 þ log 1:0Þ HCl (10 3 Eq/L) would have a pH of 3.0.
¼ 6:8 By solving the dissociation equilibrium equation for
þ
[H ], the same can be shown:
Consider adding 1 mmol of HCl to this solution. The
protons from the HCl are donated to the salt of the buffer ½HA
þ
½H ¼ K a
pair (Na 2 HPO 4 ), converting it to its conjugate acid ½A
(NaH 2 PO 4 ). If 10 mmol of each phosphate salt was