Page 216 - Feline Cardiology
P. 216
Chapter 18: Arrhythmias and Other Electrocardiographic Abnormalities 221
II
QRS
QRS QRS
* * *
T P T
P P′ T
A
* T P
QRS Arrhythmias
B
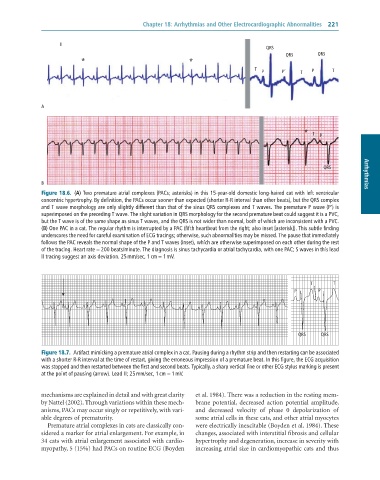
Figure 18.6. (A) Two premature atrial complexes (PACs; asterisks) in this 15-year-old domestic long-haired cat with left ventricular
concentric hypertrophy. By definition, the PACs occur sooner than expected (shorter R-R interval than other beats), but the QRS complex
and T wave morphology are only slightly different than that of the sinus QRS complexes and T waves. The premature P wave (P’) is
superimposed on the preceding T wave. The slight variation in QRS morphology for the second premature beat could suggest it is a PVC,
but the T wave is of the same shape as sinus T waves, and the QRS is not wider than normal, both of which are inconsistent with a PVC.
(B) One PAC in a cat. The regular rhythm is interrupted by a PAC (fifth heartbeat from the right; also inset [asterisk]). This subtle finding
underscores the need for careful examination of ECG tracings; otherwise, such abnormalities may be missed. The pause that immediately
follows the PAC reveals the normal shape of the P and T waves (inset), which are otherwise superimposed on each other during the rest
of the tracing. Heart rate = 200 beats/minute. The diagnosis is sinus tachycardia or atrial tachycardia, with one PAC; S waves in this lead
II tracing suggest an axis deviation. 25 mm/sec, 1 cm = 1 mV.
T T
P P
QRS QRS
Figure 18.7. Artifact mimicking a premature atrial complex in a cat. Pausing during a rhythm strip and then restarting can be associated
with a shorter R-R interval at the time of restart, giving the erroneous impression of a premature beat. In this figure, the ECG acquisition
was stopped and then restarted between the first and second beats. Typically, a sharp vertical line or other ECG stylus marking is present
at the point of pausing (arrow). Lead II; 25 mm/sec, 1 cm = 1 mV.
mechanisms are explained in detail and with great clarity et al. 1984). There was a reduction in the resting mem-
by Nattel (2002). Through variations within these mech- brane potential, decreased action potential amplitude,
anisms, PACs may occur singly or repetitively, with vari- and decreased velocity of phase 0 depolarization of
able degrees of prematurity. some atrial cells in these cats, and other atrial myocytes
Premature atrial complexes in cats are classically con- were electrically inexcitable (Boyden et al. 1984). These
sidered a marker for atrial enlargement. For example, in changes, associated with interstitial fibrosis and cellular
34 cats with atrial enlargement associated with cardio- hypertrophy and degeneration, increase in severity with
myopathy, 5 (15%) had PACs on routine ECG (Boyden increasing atrial size in cardiomyopathic cats and thus