Page 133 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 133
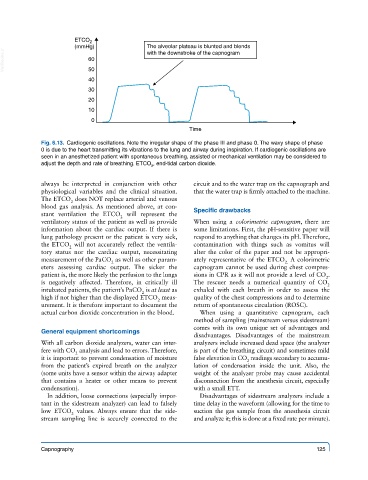
ETCO 2
(mmHg) The alveolar plateau is blunted and blends
VetBooks.ir 60
with the downstroke of the capnogram
50
40
30
20
10
0
Time
Fig. 6.13. Cardiogenic oscillations. Note the irregular shape of the phase III and phase 0. The wavy shape of phase
0 is due to the heart transmitting its vibrations to the lung and airway during inspiration. If cardiogenic oscillations are
seen in an anesthetized patient with spontaneous breathing, assisted or mechanical ventilation may be considered to
adjust the depth and rate of breathing. ETCO , end-tidal carbon dioxide.
2
always be interpreted in conjunction with other circuit and to the water trap on the capnograph and
physiological variables and the clinical situation. that the water trap is firmly attached to the machine.
The ETCO does NOT replace arterial and venous
2
blood gas analysis. As mentioned above, at con-
stant ventilation the ETCO will represent the Specific drawbacks
2
ventilatory status of the patient as well as provide When using a colorimetric capnogram, there are
information about the cardiac output. If there is some limitations. First, the pH-sensitive paper will
lung pathology present or the patient is very sick, respond to anything that changes its pH. Therefore,
the ETCO will not accurately reflect the ventila- contamination with things such as vomitus will
2
tory status nor the cardiac output, necessitating alter the color of the paper and not be appropri-
measurement of the PaCO as well as other param- ately representative of the ETCO A colorimetric
2.
2
eters assessing cardiac output. The sicker the capnogram cannot be used during chest compres-
patient is, the more likely the perfusion to the lungs sions in CPR as it will not provide a level of CO .
2
is negatively affected. Therefore, in critically ill The rescuer needs a numerical quantity of CO
2
intubated patients, the patient’s PaCO is at least as exhaled with each breath in order to assess the
2
high if not higher than the displayed ETCO meas- quality of the chest compressions and to determine
2
urement. It is therefore important to document the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
actual carbon dioxide concentration in the blood. When using a quantitative capnogram, each
method of sampling (mainstream versus sidestream)
comes with its own unique set of advantages and
General equipment shortcomings
disadvantages. Disadvantages of the mainstream
With all carbon dioxide analyzers, water can inter- analyzers include increased dead space (the analyzer
fere with CO analysis and lead to errors. Therefore, is part of the breathing circuit) and sometimes mild
2
it is important to prevent condensation of moisture false elevation in CO readings secondary to accumu-
2
from the patient’s expired breath on the analyzer lation of condensation inside the unit. Also, the
(some units have a sensor within the airway adapter weight of the analyzer probe may cause accidental
that contains a heater or other means to prevent disconnection from the anesthesia circuit, especially
condensation). with a small ETT.
In addition, loose connections (especially impor- Disadvantages of sidestream analyzers include a
tant in the sidestream analyzer) can lead to falsely time delay in the waveform (allowing for the time to
low ETCO values. Always ensure that the side- suction the gas sample from the anesthesia circuit
2
stream sampling line is securely connected to the and analyze it; this is done at a fixed rate per minute).
Capnography 125