Page 129 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 129
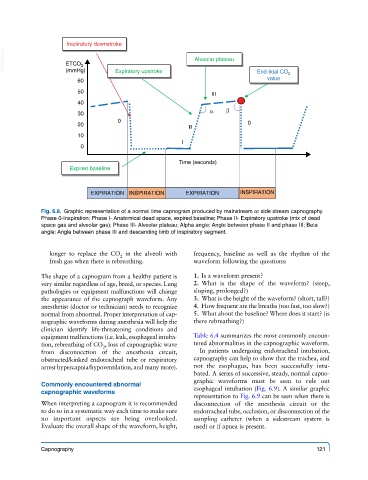
Inspiratory downstroke
VetBooks.ir ETCO 2 Alveolar plateau
(mmHg)
value
60 Expiratory upstroke End-tidal CO 2
50 III
40
30 α β
0 0
20
II
10
I
0
Time (seconds)
Expired baseline
EXPIRATION INSPIRATION EXPIRATION INSPIRATION
Fig. 6.8. Graphic representation of a normal time capnogram produced by mainstream or side stream capnography.
Phase 0-Inspiration; Phase I- Anatomical dead space, expired baseline; Phase II- Expiratory upstroke (mix of dead
space gas and alveolar gas); Phase III- Alveolar plateau; Alpha angle: Angle between phase II and phase III; Beta
angle: Angle between phase III and descending limb of inspiratory segment.
longer to replace the CO in the alveoli with frequency, baseline as well as the rhythm of the
2
fresh gas when there is rebreathing. waveform following the questions:
The shape of a capnogram from a healthy patient is 1. Is a waveform present?
very similar regardless of age, breed, or species. Lung 2. What is the shape of the waveform? (steep,
pathologies or equipment malfunctions will change sloping, prolonged?)
the appearance of the capnograph waveform. Any 3. What is the height of the waveform? (short, tall?)
anesthetist (doctor or technician) needs to recognize 4. How frequent are the breaths (too fast, too slow?)
normal from abnormal. Proper interpretation of cap- 5. What about the baseline? Where does it start? (is
nographic waveforms during anesthesia will help the there rebreathing?)
clinician identify life-threatening conditions and
equipment malfunctions (i.e. leak, esophageal intuba- Table 6.4 summarizes the most commonly encoun-
tion, rebreathing of CO , loss of capnographic wave tered abnormalities in the capnographic waveform.
2
from disconnection of the anesthesia circuit, In patients undergoing endotracheal intubation,
obstructed/kinked endotracheal tube or respiratory capnography can help to show that the trachea, and
arrest hypercapnia/hypoventilation, and many more). not the esophagus, has been successfully intu-
bated. A series of successive, steady, normal capno-
graphic waveforms must be seen to rule out
Commonly encountered abnormal
capnographic waveforms esophageal intubation (Fig. 6.9). A similar graphic
representation to Fig. 6.9 can be seen when there is
When interpreting a capnogram it is recommended disconnection of the anesthesia circuit or the
to do so in a systematic way each time to make sure endotracheal tube, occlusion, or disconnection of the
no important aspects are being overlooked. sampling catheter (when a sidestream system is
Evaluate the overall shape of the waveform, height, used) or if apnea is present.
Capnography 121