Page 130 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 130
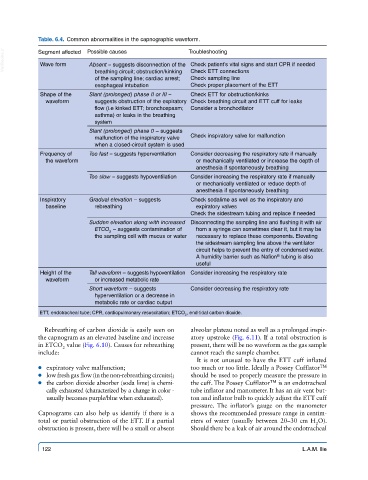
Table. 6.4. Common abnormalities in the capnographic waveform.
VetBooks.ir Segment affected Possible causes Troubleshooting
Wave form
Absent – suggests disconnection of the Check patient’s vital signs and start CPR if needed
breathing circuit; obstruction/kinking
Check sampling line
of the sampling line; cardiac arrest; Check ETT connections
esophageal intubation Check proper placement of the ETT
Shape of the Slant (prolonged) phase II or III – Check ETT for obstruction/kinks
waveform suggests obstruction of the expiratory Check breathing circuit and ETT cuff for leaks
flow (i.e kinked ETT; bronchospasm; Consider a bronchodilator
asthma) or leaks in the breathing
system
Slant (prolonged) phase 0 – suggests
malfunction of the inspiratory valve Check inspiratory valve for malfunction
when a closed-circuit system is used
Frequency of Too fast – suggests hyperventilation Consider decreasing the respiratory rate if manually
the waveform or mechanically ventilated or increase the depth of
anesthesia if spontaneously breathing
Too slow – suggests hypoventilation Consider increasing the respiratory rate if manually
or mechanically ventilated or reduce depth of
anesthesia if spontaneously breathing
Inspiratory Gradual elevation – suggests Check sodalime as well as the inspiratory and
baseline rebreathing expiratory valves
Check the sidestream tubing and replace if needed
Sudden elevation along with increased Disconnecting the sampling line and flushing it with air
ETCO – suggests contamination of from a syringe can sometimes clear it, but it may be
2
the sampling cell with mucus or water necessary to replace these components. Elevating
the sidestream sampling line above the ventilator
circuit helps to prevent the entry of condensed water.
A humidity barrier such as Nafion tubing is also
®
useful
Height of the Tall waveform – suggests hypoventilation Consider increasing the respiratory rate
waveform or increased metabolic rate
Short waveform – suggests Consider decreasing the respiratory rate
hyperventilation or a decrease in
metabolic rate or cardiac output
ETT, endotracheal tube; CPR, cardiopulmonary resuscitation; ETCO , end-tidal carbon dioxide.
2
Rebreathing of carbon dioxide is easily seen on alveolar plateau noted as well as a prolonged inspir-
the capnogram as an elevated baseline and increase atory upstroke (Fig. 6.11). If a total obstruction is
in ETCO value (Fig. 6.10). Causes for rebreathing present, there will be no waveform as the gas sample
2
include: cannot reach the sample chamber.
It is not unusual to have the ETT cuff inflated
● ● expiratory valve malfunction; too much or too little. Ideally a Possey Cufflator TM
● ● low fresh gas flow (in the non-rebreathing circuits); should be used to properly measure the pressure in
● ● the carbon dioxide absorber (soda lime) is chemi- the cuff. The Possey Cufflator TM is an endotracheal
cally exhausted (characterized by a change in color - tube inflator and manometer. It has an air vent but-
usually becomes purple/blue when exhausted). ton and inflator bulb to quickly adjust the ETT cuff
pressure. The inflator’s gauge on the manometer
Capnograms can also help us identify if there is a shows the recommended pressure range in centim-
total or partial obstruction of the ETT. If a partial eters of water (usually between 20–30 cm H O).
2
obstruction is present, there will be a small or absent Should there be a leak of air around the endotracheal
122 L.A.M. Ilie