Page 155 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 155
122 SECTION | I General
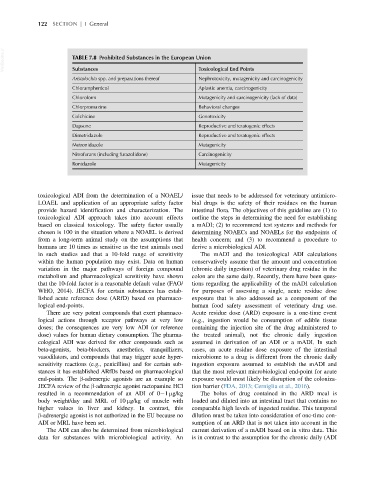
VetBooks.ir TABLE 7.8 Prohibited Substances in the European Union
Toxicological End Points
Substances
Aristolochia spp. and preparations thereof Nephrotoxicity, mutagenicity and carcinogenicity
Chloramphenicol Aplastic anemia, carcinogenicity
Chloroform Mutagenicity and carcinogenicity (lack of data)
Chlorpromazine Behavioral changes
Colchicine Genotoxicity
Dapsone Reproductive and teratogenic effects
Dimetridazole Reproductive and teratogenic effects
Metronidazole Mutagenicity
Nitrofurans (including furazolidone) Carcinogenicity
Ronidazole Mutagenicity
toxicological ADI from the determination of a NOAEL/ issue that needs to be addressed for veterinary antimicro-
LOAEL and application of an appropriate safety factor bial drugs is the safety of their residues on the human
provide hazard identification and characterization. The intestinal flora. The objectives of this guideline are (1) to
toxicological ADI approach takes into account effects outline the steps in determining the need for establishing
based on classical toxicology. The safety factor usually a mADI; (2) to recommend test systems and methods for
chosen is 100 in the situation where a NOAEL is derived determining NOAECs and NOAELs for the endpoints of
from a long-term animal study on the assumptions that health concern; and (3) to recommend a procedure to
humans are 10 times as sensitive as the test animals used derive a microbiological ADI.
in such studies and that a 10-fold range of sensitivity The mADI and the toxicological ADI calculations
within the human population may exist. Data on human conservatively assume that the amount and concentration
variation in the major pathways of foreign compound (chronic daily ingestion) of veterinary drug residue in the
metabolism and pharmacological sensitivity have shown colon are the same daily. Recently, there have been ques-
that the 10-fold factor is a reasonable default value (FAO/ tions regarding the applicability of the mADI calculation
WHO, 2014). JECFA for certain substances has estab- for purposes of assessing a single, acute residue dose
lished acute reference dose (ARfD) based on pharmaco- exposure that is also addressed as a component of the
logical end-points. human food safety assessment of veterinary drug use.
There are very potent compounds that exert pharmaco- Acute residue dose (ARD) exposure is a one-time event
logical actions through receptor pathways at very low (e.g., ingestion would be consumption of edible tissue
doses; the consequences are very low ADI (or reference containing the injection site of the drug administered to
dose) values for human dietary consumption. The pharma- the treated animal), not the chronic daily ingestion
cological ADI was derived for other compounds such as assumed in derivation of an ADI or a mADI. In such
beta-agonists, beta-blockers, anesthetics, tranquillizers, cases, an acute residue dose exposure of the intestinal
vasodilators, and compounds that may trigger acute hyper- microbiome to a drug is different from the chronic daily
sensitivity reactions (e.g., penicillins) and for certain sub- ingestion exposure assumed to establish the mADI and
stances it has established ARfDs based on pharmacological that the most relevant microbiological end-point for acute
end-points. The β-adrenergic agonists are an example so exposure would most likely be disruption of the coloniza-
JECFAreviewof the β-adrenergic agonist ractopamine HCl tion barrier (FDA, 2013; Cerniglia et al., 2016).
resulted in a recommendation of an ADI of 0 1 μg/kg The bolus of drug contained in the ARD meal is
body weight/day and MRL of 10 μg/kg of muscle with loaded and diluted into an intestinal tract that contains no
higher values in liver and kidney. In contrast, this comparable high levels of ingested residue. This temporal
β-adrenergic agonist is not authorized in the EU because no dilution must be taken into consideration of one-time con-
ADI or MRL have been set. sumption of an ARD that is not taken into account in the
The ADI can also be determined from microbiological current derivation of a mADI based on in vitro data. This
data for substances with microbiological activity. An is in contrast to the assumption for the chronic daily (ADI