Page 158 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 158
Regulatory Aspects for the Drugs and Chemicals Used in Food-Producing Animals Chapter | 7 125
VetBooks.ir JMPR residue evaluation
Metabolism &
distribution studies Residues for Marker (“enforcement”)
risk assessment residue
Field trials & GAp LMR
STMR; HR
Recommend MRL,
state if ADI or ARfD
Intake > ADI; ARfD
is exceeded
Intake assessment
(regional/national diets)
Intake ≤ ADI; ARfD Recommend MRL
JECFA residue evaluation
Metabolism &
distribution studies Marker residue Total residue
Field trials & GPVD Residue depletion curve
& confidence interval MRL
Median residue
ADI 1. Estimate 2. Estimate
Adjust MRL MRL not recommended
Intake assessment Intake > ADI
(Model food basket)
Intake ≤ ADI Accept MRL Option to adjust MRL
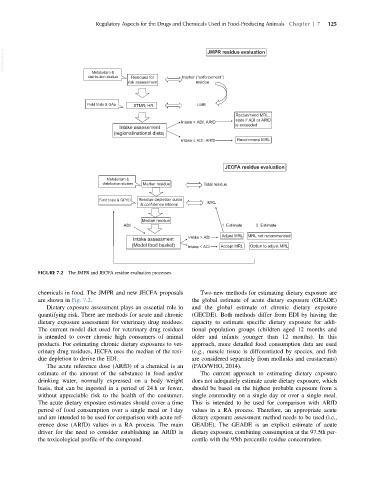
FIGURE 7.2 The JMPR and JECFA residue evaluation processes.
chemicals in food. The JMPR and new JECFA proposals Two new methods for estimating dietary exposure are
are shown in Fig. 7.2. the global estimate of acute dietary exposure (GEADE)
Dietary exposure assessment plays an essential role in and the global estimate of chronic dietary exposure
quantifying risk. There are methods for acute and chronic (GECDE). Both methods differ from EDI by having the
dietary exposure assessment for veterinary drug residues. capacity to estimate specific dietary exposure for addi-
The current model diet used for veterinary drug residues tional population groups (children aged 12 months and
is intended to cover chronic high consumers of animal older and infants younger than 12 months). In this
products. For estimating chronic dietary exposures to vet- approach, more detailed food consumption data are used
erinary drug residues, JECFA uses the median of the resi- (e.g., muscle tissue is differentiated by species, and fish
due depletion to derive the EDI. are considered separately from mollusks and crustaceans)
The acute reference dose (ARfD) of a chemical is an (FAO/WHO, 2014).
estimate of the amount of the substance in food and/or The current approach to estimating dietary exposure
drinking water, normally expressed on a body weight does not adequately estimate acute dietary exposure, which
basis, that can be ingested in a period of 24 h or fewer, should be based on the highest probable exposure from a
without appreciable risk to the health of the consumer. single commodity on a single day or over a single meal.
The acute dietary exposure estimates should cover a time This is intended to be used for comparison with ARfD
period of food consumption over a single meal or 1 day values in a RA process. Therefore, an appropriate acute
and are intended to be used for comparison with acute ref- dietary exposure assessment method needs to be used (i.e.,
erence dose (ARfD) values in a RA process. The main GEADE). The GEADE is an explicit estimate of acute
driver for the need to consider establishing an ARfD is dietary exposure, combining consumption at the 97.5th per-
the toxicological profile of the compound. centile with the 95th percentile residue concentration.