Page 620 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 620
Anticoagulant Chapter | 46 585
VetBooks.ir 2. Indanediones. This group of compounds has a newer and more potent second-generation anticoagulant
rodenticides. It was introduced in 1977 by Sorex Ltd. of
1,3-indanedione structure, with different side-chain
London, then developed by the Imperial Chemicals
substituents at the 2-position. The most common anti-
coagulant rodenticides in this group are chlorophaci- Incorporated (ICI) Plant Protection Division
none and diphacinone. Examples of each of these (Chalermchaikit et al., 1993).
compounds are briefly summarized. Pure brodifacoum is off-white to fawn-colored pow-
der, with a solubility of 6 20 g/L in acetone, 3 g/L in
A few representative chemicals are described below.
chloroform, 0.6 6 g/L in benzene, and less than 10 mg/L
A number of other chemicals have now been developed.
in water. It is very stable in the environment, with no
loss after 30 days of exposure to direct sunlight
(Chalermchaikit et al., 1993).
Hydroxycoumarins
Brodifacoum has been marketed in several countries
Bromadiolone for the control of a wide range of rodent pest species. It is
available as a 0.005% pellet for rat and house mouse con-
trols, a smaller 0.001% pellet for field rodent control, and
as 29 g wax blocks for sewer rat control. It was the only
anticoagulant rodenticide reported to produce 100%
OH OH mortality in most rodent species after a 24 h dose.
Although brodifacoum was effective against warfarin-
resistant rats and mice in 1984, the possibility of resis-
tance has been raised (Lund, 1984).
O O Variation occurs in the susceptibility of species to
brodifacoum. The average pig, sheep, or chicken must
Br consume considerable quantities of prepared bait to be
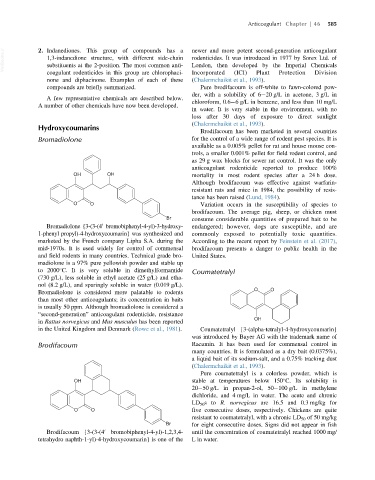
Bromadiolone {3-(3-(4 bromobiphenyl-4-yl)-3-hydroxy- endangered; however, dogs are susceptible, and are
0
1-phenyl propyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin} was synthesized and commonly exposed to potentially toxic quantities.
marketed by the French company Lipha S.A. during the According to the recent report by Feinstein et al. (2017),
mid-1970s. It is used widely for control of commensal brodifacoum presents a danger to public health in the
and field rodents in many countries. Technical grade bro- United States.
madiolone is a 97% pure yellowish powder and stable up
to 2000 C. It is very soluble in dimethylformamide Coumatetralyl
(730 g/L), less soluble in ethyl acetate (25 g/L) and etha-
nol (8.2 g/L), and sparingly soluble in water (0.019 g/L).
O O
Bromadiolone is considered more palatable to rodents
than most other anticoagulants; its concentration in baits
is usually 50 ppm. Although bromadiolone is considered a
“second-generation” anticoagulant rodenticide, resistance
OH
in Rattus norvegicus and Mus musculus has been reported
in the United Kingdom and Denmark (Rowe et al., 1981). Coumatetralyl {3-(alpha-tetralyl-4-hydroxycoumarin}
was introduced by Bayer AG with the trademark name of
Brodifacoum Racumin. It has been used for commensal control in
many countries. It is formulated as a dry bait (0.0375%),
a liquid bait of its sodium-salt, and a 0.75% tracking dust
(Chalermchaikit et al., 1993).
Pure coumatetralyl is a colorless powder, which is
OH stable at temperatures below 150 C. Its solubility is
20 50 g/L in propan-2-ol, 50 100 g/L in methylene
dichloride, and 4 mg/L in water. The acute and chronic
LD 50 sto R. norvegicus are 16.5 and 0.3 mg/kg for
O O five consecutive doses, respectively. Chickens are quite
resistant to coumatetralyl, with a chronic LD 50 of 50 mg/kg
Br for eight consecutive doses. Signs did not appear in fish
Brodifacoum {3-(3-(4 0 bromobiphenyl-4-yl)-1,2,3,4- until the concentration of coumatetralyl reached 1000 mg/
tetrahydro naphth-1-yl)-4-hydroxycoumarin} is one of the L in water.