Page 1240 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1240
1212 PART XI Immune-Mediated Disorders
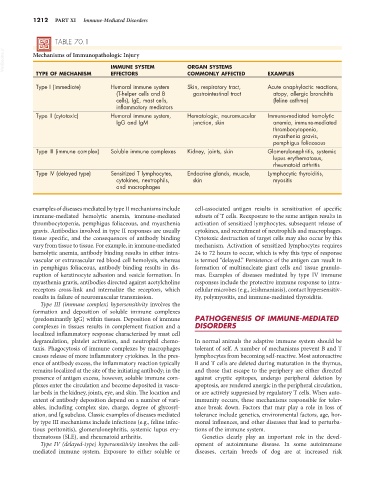
TABLE 70.1
VetBooks.ir Mechanisms of Immunopathologic Injury ORGAN SYSTEMS
IMMUNE SYSTEM
TYPE OF MECHANISM EFFECTORS COMMONLY AFFECTED EXAMPLES
Type I (immediate) Humoral immune system Skin, respiratory tract, Acute anaphylactic reactions,
(T-helper cells and B gastrointestinal tract atopy, allergic bronchitis
cells), IgE, mast cells, (feline asthma)
inflammatory mediators
Type II (cytotoxic) Humoral immune system, Hematologic, neuromuscular Immune-mediated hemolytic
IgG and IgM junction, skin anemia, immune-mediated
thrombocytopenia,
myasthenia gravis,
pemphigus foliaceous
Type III (immune complex) Soluble immune complexes Kidney, joints, skin Glomerulonephritis, systemic
lupus erythematosus,
rheumatoid arthritis
Type IV (delayed type) Sensitized T lymphocytes, Endocrine glands, muscle, Lymphocytic thyroiditis,
cytokines, neutrophils, skin myositis
and macrophages
examples of diseases mediated by type II mechanisms include cell-associated antigen results in sensitization of specific
immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, immune-mediated subsets of T cells. Reexposure to the same antigen results in
thrombocytopenia, pemphigus foliaceous, and myasthenia activation of sensitized lymphocytes, subsequent release of
gravis. Antibodies involved in type II responses are usually cytokines, and recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages.
tissue specific, and the consequences of antibody binding Cytotoxic destruction of target cells may also occur by this
vary from tissue to tissue. For example, in immune-mediated mechanism. Activation of sensitized lymphocytes requires
hemolytic anemia, antibody binding results in either intra- 24 to 72 hours to occur, which is why this type of response
vascular or extravascular red blood cell hemolysis, whereas is termed “delayed.” Persistence of the antigen can result in
in pemphigus foliaceous, antibody binding results in dis- formation of multinucleate giant cells and tissue granulo-
ruption of keratinocyte adhesion and vesicle formation. In mas. Examples of diseases mediated by type IV immune
myasthenia gravis, antibodies directed against acetylcholine responses include the protective immune response to intra-
receptors cross-link and internalize the receptors, which cellular microbes (e.g., leishmaniasis), contact hypersensitiv-
results in failure of neuromuscular transmission. ity, polymyositis, and immune-mediated thyroiditis.
Type III (immune complex) hypersensitivity involves the
formation and deposition of soluble immune complexes
(predominantly IgG) within tissues. Deposition of immune PATHOGENESIS OF IMMUNE-MEDIATED
complexes in tissues results in complement fixation and a DISORDERS
localized inflammatory response characterized by mast cell
degranulation, platelet activation, and neutrophil chemo- In normal animals the adaptive immune system should be
taxis. Phagocytosis of immune complexes by macrophages tolerant of self. A number of mechanisms prevent B and T
causes release of more inflammatory cytokines. In the pres- lymphocytes from becoming self-reactive. Most autoreactive
ence of antibody excess, the inflammatory reaction typically B and T cells are deleted during maturation in the thymus,
remains localized at the site of the initiating antibody; in the and those that escape to the periphery are either directed
presence of antigen excess, however, soluble immune com- against cryptic epitopes, undergo peripheral deletion by
plexes enter the circulation and become deposited in vascu- apoptosis, are rendered anergic in the peripheral circulation,
lar beds in the kidney, joints, eye, and skin. The location and or are actively suppressed by regulatory T cells. When auto-
extent of antibody deposition depend on a number of vari- immunity occurs, these mechanisms responsible for toler-
ables, including complex size, charge, degree of glycosyl- ance break down. Factors that may play a role in loss of
ation, and Ig subclass. Classic examples of diseases mediated tolerance include genetics, environmental factors, age, hor-
by type III mechanisms include infections (e.g., feline infec- monal influences, and other diseases that lead to perturba-
tious peritonitis), glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus ery- tions of the immune system.
thematosus (SLE), and rheumatoid arthritis. Genetics clearly play an important role in the devel-
Type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity involves the cell- opment of autoimmune disease. In some autoimmune
mediated immune system. Exposure to either soluble or diseases, certain breeds of dog are at increased risk