Page 1241 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1241
CHAPTER 70 Pathogenesis of Immune-Mediated Disorders 1213
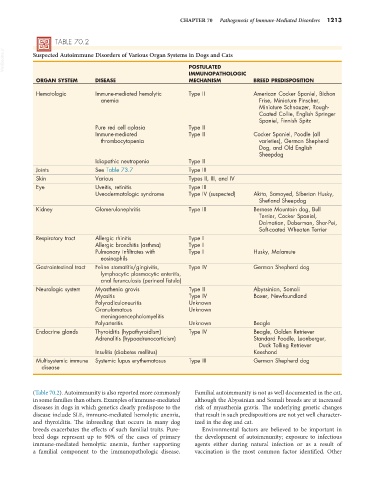
TABLE 70.2
VetBooks.ir Suspected Autoimmune Disorders of Various Organ Systems in Dogs and Cats
POSTULATED
IMMUNOPATHOLOGIC
ORGAN SYSTEM DISEASE MECHANISM BREED PREDISPOSITION
Hematologic Immune-mediated hemolytic Type II American Cocker Spaniel, Bichon
anemia Frise, Miniature Pinscher,
Miniature Schnauzer, Rough-
Coated Collie, English Springer
Spaniel, Finnish Spitz
Pure red cell aplasia Type II
Immune-mediated Type II Cocker Spaniel, Poodle (all
thrombocytopenia varieties), German Shepherd
Dog, and Old English
Sheepdog
Idiopathic neutropenia Type II
Joints See Table 73.7 Type III
Skin Various Types II, III, and IV
Eye Uveitis, retinitis Type III
Uveodermatologic syndrome Type IV (suspected) Akita, Samoyed, Siberian Husky,
Shetland Sheepdog
Kidney Glomerulonephritis Type III Bernese Mountain dog, Bull
Terrier, Cocker Spaniel,
Dalmatian, Doberman, Shar-Pei,
Soft-coated Wheaten Terrier
Respiratory tract Allergic rhinitis Type I
Allergic bronchitis (asthma) Type I
Pulmonary infiltrates with Type I Husky, Malamute
eosinophils
Gastrointestinal tract Feline stomatitis/gingivitis, Type IV German Shepherd dog
lymphocytic plasmacytic enteritis,
anal furunculosis (perineal fistula)
Neurologic system Myasthenia gravis Type II Abyssinian, Somali
Myositis Type IV Boxer, Newfoundland
Polyradiculoneuritis Unknown
Granulomatous Unknown
meningoencephalomyelitis
Polyarteritis Unknown Beagle
Endocrine glands Thyroiditis (hypothyroidism) Type IV Beagle, Golden Retriever
Adrenalitis (hypoadrenocorticism) Standard Poodle, Leonberger,
Duck Tolling Retriever
Insulitis (diabetes mellitus) Keeshond
Multisystemic immune Systemic lupus erythematosus Type III German Shepherd dog
disease
(Table 70.2). Autoimmunity is also reported more commonly Familial autoimmunity is not as well documented in the cat,
in some families than others. Examples of immune-mediated although the Abyssinian and Somali breeds are at increased
diseases in dogs in which genetics clearly predispose to the risk of myasthenia gravis. The underlying genetic changes
disease include SLE, immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, that result in such predispositions are not yet well character-
and thyroiditis. The inbreeding that occurs in many dog ized in the dog and cat.
breeds exacerbates the effects of such familial traits. Pure- Environmental factors are believed to be important in
bred dogs represent up to 90% of the cases of primary the development of autoimmunity; exposure to infectious
immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, further supporting agents either during natural infection or as a result of
a familial component to the immunopathologic disease. vaccination is the most common factor identified. Other