Page 762 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 762
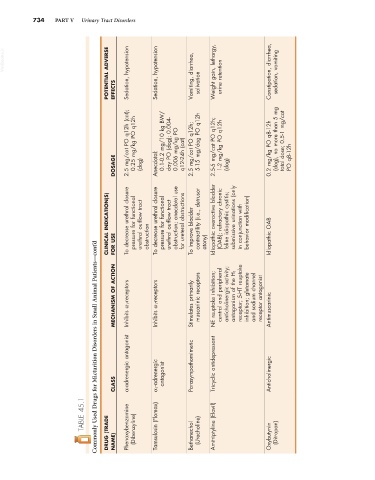
734 PART V Urinary Tract Disorders
POTENTIAL ADVERSE EFFECTS Sedation, hypotension Sedation, hypotension Vomiting, diarrhea, salivation Weight gain, lethargy, urine retention Constipation, diarrhea, sedation, vomiting
VetBooks.ir
2.5 mg/cat PO q12h (cat); 0.25 mg/kg PO q12h 0.1-0.2 mg/10 kg BW/ day PO (dog); 0.004- 0.006 mg/kg PO 2.5 mg/cat PO q12h; 5-15 mg/dog PO q12h 2.5-5 mg/cat PO q12h; 1-2 mg/kg PO q12h 0.2 mg/kg PO q8-12h (dog), no more than 5 mg total dose; 0.5-1 mg/cat
DOSAGE (dog) Anecdotal: q12-24h (cat) (dog) PO q8-12h
CLINICAL INDICATION(S) FOR USE To decrease urethral closure pressure for functional urethral outflow tract obstruction To decrease urethral closure pressure for functional urethral outflow tract obstruction; anecdotal use for ureteral obstructions To improve bladder contractility (i.e., detrusor atony) Idiopathic overactive bladder (OAB); refractory chronic feline idiopathic cystitis; submissive urinations (only in conjun
Commonly Used Drugs for Micturition Disorders in Small Animal Patients—cont’d
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits α 1-receptors Inhibits α 1 -receptors Stimulates primarily muscarinic receptors NE reuptake inhibition; central and peripheral anticholinergic activity; antagonism of the H 1 receptor; 5-HT reuptake inhibition; glutamate and sodium channel receptor antagonist Antimuscarinic
α-adrenergic antagonist Parasympathomimetic Tricyclic antidepressant
CLASS α 1 -adrenergic antagonist Anticholinergic
TABLE 45.1 DRUG (TRADE NAME) Phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline) Tamsulosin (Flomax) Bethanechol (Urecholine) Amitriptyline (Elavil) Oxybutynin (Ditropan)