Page 256 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 256
CHAPTER 14 Cancer Immunotherapy 235
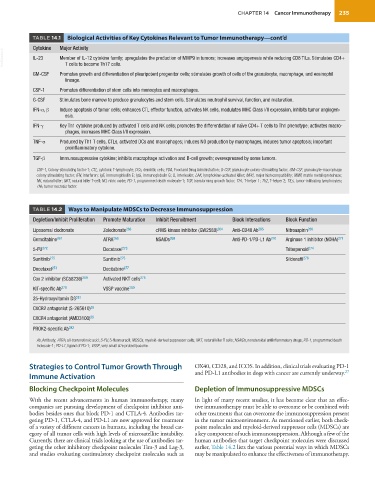
TABLE 14.1 Biological Activities of Key Cytokines Relevant to Tumor Immunotherapy—cont’d
Cytokine Major Activity
VetBooks.ir IL-23 Member of IL-12 cytokine family; upregulates the production of MMP9 in tumors; increases angiogenesis while reducing CD8 TILs. Stimulates CD4+
T cells to become Th17 cells.
GM-CSF Promotes growth and differentiation of pleuripotent progenitor cells; stimulates growth of cells of the granulocyte, macrophage, and eosinophil
lineage.
CSF-1 Promotes differentiation of stem cells into monocytes and macrophages.
G-CSF Stimulates bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells. Stimulates neutrophil survival, function, and maturation.
IFN-α, β Induce apoptosis of tumor cells; enhances CTL effector function, activates NK cells, modulates MHC Class I/II expression, inhibits tumor angiogen-
esis.
IFN-γ Key Th1 cytokine produced by activated T cells and NK cells; promotes the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells to Th1 phenotype; activates macro-
phages, increases MHC Class I/II expression.
TNF-α Produced by Th1 T cells, CTLs, activated DCs and macrophages; induces NO production by macrophages, induces tumor apoptosis; important
proinflammatory cytokine.
TGF-β Immunosuppressive cytokine; inhibits macrophage activation and B-cell growth; overexpressed by some tumors.
CSF-1, Colony-stimulating factor-1; CTL, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte; DCs, dendritic cells; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage
colony stimulating factor; IFN, interferon; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IL, interleukin; LAK, lymphokine-activated killer; MHC, major histocompatibility; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase;
NK, natural killer; NKT, natural killer T-cell; NO, nitric oxide; PD-1, programmed death molecule-1; TGF, transforming growth factor; Th1, T-helper 1; Th2, T-helper 2; TILs, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes;
TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
TABLE 14.2 Ways to Manipulate MDSCs to Decrease Immunosuppression
Depletion/Inhibit Proliferation Promote Maturation Inhibit Recruitment Block Interactions Block Function
Liposomal clodronate Zoledronate 263 cFMS kinase inhibitor (GW2580) 264 Anti-CD40 Ab 265 Nitroaspirin 266
Gemcitabine 267 ATRA 268 NSAIDs 269 Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Ab 270 Arginase 1 inhibitor (NOHA) 271
5-FU 272 Docetaxel 273 Triterpenoid 274
Sunitinib 275 Sunitinib 275 Sildenafil 276
Docetaxel 273 Decitabine 277
Cox 2 inhibitor (SC58236) 269 Activated NKT cells 278
KIT-specific Ab 279 VSSP vaccine 280
25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 281
CXCR2 antagonist (S-265610) 55
CXCR4 antagonist (AMD3100) 55
PROK2-specific Ab 282
Ab, Antibody; ATRA, all-trans retinoic acid; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; NKT, natural killer T cells; NSAIDs, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs; PD-1, programmed death
molecule-1; PD-L1, ligand of PD-1; VSSP, very small size proteoliposome.
Strategies to Control Tumor Growth Through OX40, CD28, and ICOS. In addition, clinical trials evaluating PD-1
27
Immune Activation and PD-L1 antibodies in dogs with cancer are currently underway.
Blocking Checkpoint Molecules Depletion of Immunosuppressive MDSCs
With the recent advancements in human immunotherapy, many In light of many recent studies, it has become clear that an effec-
companies are pursuing development of checkpoint inhibitor anti- tive immunotherapy must be able to overcome or be combined with
bodies besides ones that block PD-1 and CTLA-4. Antibodies tar- other treatments that can overcome the immunosuppression present
geting PD-1, CTLA-4, and PD-L1 are now approved for treatment in the tumor microenvironment. As mentioned earlier, both check-
of a variety of different cancers in humans, including the broad cat- point molecules and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are
egory of all tumor cells with high levels of microsatellite instability. a key component of such immunosuppression. Although a few of the
Currently, there are clinical trials looking at the use of antibodies tar- human antibodies that target checkpoint molecules were discussed
geting the other inhibitory checkpoint molecules Tim-3 and Lag-3, earlier, Table 14.2 lists the various potential ways in which MDSCs
and studies evaluating costimulatory checkpoint molecules such as may be manipulated to enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy.