Page 414 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 414
392 PART IV Specific Malignancies in the Small Animal Patient
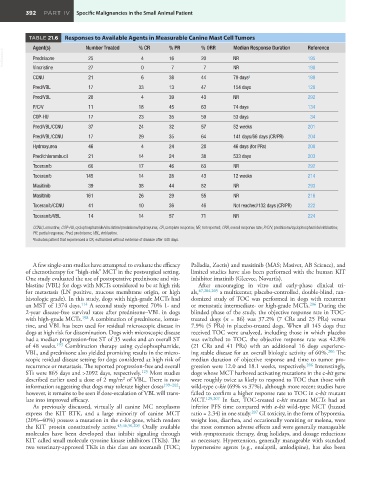
TABLE 21.6 Responses to Available Agents in Measurable Canine Mast Cell Tumors
Agent(s) Number Treated % CR % PR % ORR Median Response Duration Reference
VetBooks.ir Prednisone 25 4 0 16 7 20 7 NR 195
Vincristine
27
198
NR
CCNU 21 6 38 44 79 days a 199
Pred/VBL 17 33 13 47 154 days 128
Pred/VBL 28 4 39 43 NR 292
P/C/V 11 18 45 63 74 days 134
COP-HU 17 23 35 59 53 days 34
Pred/VBL/CCNU 37 24 32 57 52 weeks 201
Pred/VBL/CCNU 17 29 35 64 141 days/66 days (CR/PR) 204
Hydroxyurea 46 4 24 28 46 days (for PRs) 200
Pred/chlorambucil 21 14 24 38 533 days 203
Toceranib 60 17 46 63 NR 292
Toceranib 145 14 28 43 12 weeks 214
Masitinib 39 38 44 82 NR 293
Masitinib 161 26 29 55 NR 216
Toceranib/CCNU 41 10 36 46 Not reached/132 days (CR/PR) 222
Toceranib/VBL 14 14 57 71 NR 224
CCNU, Lomustine; COP-HU, cyclophosphamide/vincristine/prednisone/hydroxyurea; CR, complete response; NR, not reported; ORR, overall response rate; P/C/V, prednisone/cyclophosphamide/vinblastine;
PR, partial response; Pred, prednisone; VBL, vinblastine.
a Excludes patient that experienced a CR; euthanized without evidence of disease after 440 days.
A few single-arm studies have attempted to evaluate the efficacy Palladia, Zoetis) and masitinib (MAS; Masivet, AB Science), and
of chemotherapy for “high-risk” MCT in the postsurgical setting. limited studies have also been performed with the human KIT
One study evaluated the use of postoperative prednisone and vin- inhibitor imatinib (Gleevec, Novartis).
blastine (VBL) for dogs with MCTs considered to be at high risk After encouraging in vitro and early-phase clinical tri-
for metastasis (LN positive, mucous membrane origin, or high als, 47,204,205 a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, ran-
histologic grade). In this study, dogs with high-grade MCTs had domized study of TOC was performed in dogs with recurrent
an MST of 1374 days. 114 A second study reported 70% 1- and or metastatic intermediate- or high-grade MCTs. 206 During the
2-year disease-free survival rates after prednisone–VBL in dogs blinded phase of the study, the objective response rate in TOC-
with high-grade MCTs. 198 A combination of prednisone, lomus- treated dogs (n = 86) was 37.2% (7 CRs and 25 PRs) versus
tine, and VBL has been used for residual microscopic disease in 7.9% (5 PRs) in placebo-treated dogs. When all 145 dogs that
dogs at high risk for dissemination. Dogs with microscopic disease received TOC were analyzed, including those in which placebo
had a median progression-free ST of 35 weeks and an overall ST was switched to TOC, the objective response rate was 42.8%
of 48 weeks. 193 Combination therapy using cyclophosphamide, (21 CRs and 41 PRs) with an additional 16 dogs experienc-
VBL, and prednisone also yielded promising results in the micro- ing stable disease for an overall biologic activity of 60%. 206 The
scopic residual disease setting for dogs considered at high risk of median duration of objective response and time to tumor pro-
recurrence or metastasis. The reported progression-free and overall gression were 12.0 and 18.1 weeks, respectively. 206 Interestingly,
STs were 865 days and >2092 days, respectively. 125 Most studies dogs whose MCT harbored activating mutations in the c-kit gene
described earlier used a dose of 2 mg/m of VBL. There is now were roughly twice as likely to respond to TOC than those with
2
information suggesting that dogs may tolerate higher doses 199–202 ; wild-type c-kit (69% vs 37%), although more recent studies have
however, it remains to be seen if dose-escalation of VBL will trans- failed to confirm a higher response rate to TOC in c-kit mutant
late into improved efficacy. MCT. 129,207 In fact, TOC-treated c-kit mutant MCTs had an
As previously discussed, virtually all canine MC neoplasms inferior PFS time compared with c-kit wild-type MCT (hazard
express the KIT RTK, and a large minority of canine MCT ratio = 2.34) in one study. 207 GI toxicity, in the form of hyporexia,
(20%–40%) possess a mutation in the c-kit gene, which renders weight loss, diarrhea, and occasionally vomiting or melena, were
the KIT protein constitutively active. 43,46,50,203 Orally available the most common adverse effects and were generally manageable
molecules have been developed that inhibit signaling through with symptomatic therapy, drug holidays, and dosage reductions
KIT called small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The as necessary. Hypertension, generally manageable with standard
two veterinary-approved TKIs in this class are toceranib (TOC; hypertensive agents (e.g., enalapril, amlodipine), has also been