Page 130 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 130
116 Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
leads to a local ATP deficit, and this little crisis leads to Infraspinatus Ileocostorum
the release of inflammatory mediators. The persistence TP lumbortum TP
of nociceptive stimuli or such mediators can result in Gluteus TP
central nervous system (CNS) sensitization and hyper- medius
algesia. From a biomechanical point of view, TPs can be
the result of or can be perpetuated by trauma, whether
this is acute or a series of repetitive microtraumas due to Triceps TP
nearby articular dysfunction and postural disorders. All
of these will generate more muscle stress. Other factors
have been proposed, such as psychological stress, poor
diet, visceral pain, and coldness. [305] So, together with Quadriceps TP
its effect on inflammatory mediators and pain modula- Peroneus longus TP
tion, the efficacy of LT in treating TPs could be related
to its effect on blood flow, oxygenation, and ATP pro-
duction, which lie at the core of TP pathogenesis.
Palpation is the most common tool for assessing TPs
and it’s not a bad one: 73% of clinicians were in agree-
ment according to an inter-rater reliability study carried
out in humans. [306] Other methods have been described,
such as measuring spontaneous electrical activity, or Adductor and
pectineus TP
mechanical pressure thresholds, but let’s focus on the
tools you have closer to hand in your practice.
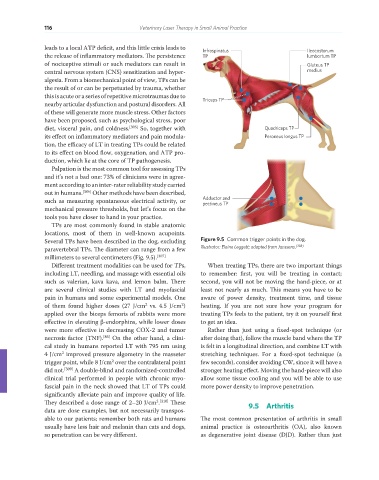
TPs are most commonly found in stable anatomic
locations, most of them in well-known acupoints.
Several TPs have been described in the dog, excluding Figure 9.5 Common trigger points in the dog.
paravertebral TPs. The diameter can range from a few Illustrator: Elaine Leggett; adapted from Janssens. [308]
millimeters to several centimeters (Fig. 9.5). [307]
Different treatment modalities can be used for TPs, When treating TPs, there are two important things
including LT, needling, and massage with essential oils to remember: first, you will be treating in contact;
such as valerian, kava kava, and lemon balm. There second, you will not be moving the hand-piece, or at
are several clinical studies with LT and myofascial least not nearly as much. This means you have to be
pain in humans and some experimental models. One aware of power density, treatment time, and tissue
of them found higher doses (27 J/cm vs. 4.5 J/cm ) heating. If you are not sure how your program for
2
2
applied over the biceps femoris of rabbits were more treating TPs feels to the patient, try it on yourself first
effective in elevating β-endorphins, while lower doses to get an idea.
were more effective in decreasing COX-2 and tumor Rather than just using a fixed-spot technique (or
necrosis factor (TNF). [86] On the other hand, a clini- after doing that), follow the muscle band where the TP
cal study in humans reported LT with 795 nm using is felt in a longitudinal direction, and combine LT with
2
4 J/cm improved pressure algometry in the masseter stretching techniques. For a fixed-spot technique (a
trigger point, while 8 J/cm over the contralateral point few seconds), consider avoiding CW, since it will have a
2
did not. [309] A double-blind and randomized-controlled stronger heating effect. Moving the hand-piece will also
clinical trial performed in people with chronic myo- allow some tissue cooling and you will be able to use
fascial pain in the neck showed that LT of TPs could more power density to improve penetration.
significantly alleviate pain and improve quality of life.
They described a dose range of 2–20 J/cm . These 9.5 Arthritis
2 [310]
data are dose examples, but not necessarily transpos-
able to our patients; remember both rats and humans The most common presentation of arthritis in small
usually have less hair and melanin than cats and dogs, animal practice is osteoarthritis (OA), also known
so penetration can be very different. as degenerative joint disease (DJD). Rather than just
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 116 08/08/2019 09:48