Page 26 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 26
12 Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
of NO available both inside and outside the cell. Besides since in that environment there is a very high “partial
its function in cell signaling, NO serves as a potent oxygen pressure” (i.e. a local surplus of oxygen). They
vasodilator when it is available outside the cell. After hold on as they travel through the body in blood vessels
all, when the body senses a threat (whether an ischemic until they find themselves in an environment with a low
event or another local stimulus), it naturally secretes enough partial oxygen pressure (i.e. a local deficiency
NO as the principle catalyst for vasodilation. of oxygen), at which point they begin to dissociate and
We’ll cover the anti-inflammatory effect in more release their oxygen locally.
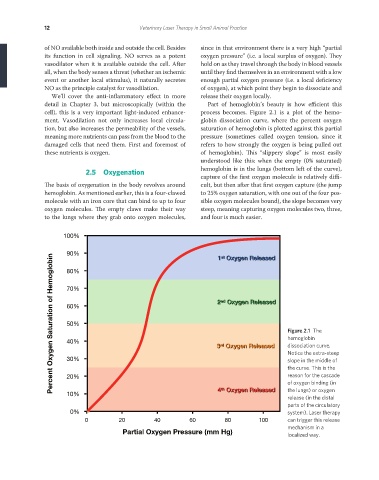
detail in Chapter 3, but microscopically (within the Part of hemoglobin’s beauty is how efficient this
cell), this is a very important light-induced enhance- process becomes. Figure 2.1 is a plot of the hemo-
ment. Vasodilation not only increases local circula- globin dissociation curve, where the percent oxygen
tion, but also increases the permeability of the vessels, saturation of hemoglobin is plotted against this partial
meaning more nutrients can pass from the blood to the pressure (sometimes called oxygen tension, since it
damaged cells that need them. First and foremost of refers to how strongly the oxygen is being pulled out
these nutrients is oxygen. of hemoglobin). This “slippery slope” is most easily
understood like this: when the empty (0% saturated)
2.5 Oxygenation hemoglobin is in the lungs (bottom left of the curve),
capture of the first oxygen molecule is relatively diffi-
The basis of oxygenation in the body revolves around cult, but then after that first oxygen capture (the jump
hemoglobin. As mentioned earlier, this is a four-clawed to 25% oxygen saturation, with one out of the four pos-
molecule with an iron core that can bind to up to four sible oxygen molecules bound), the slope becomes very
oxygen molecules. The empty claws make their way steep, meaning capturing oxygen molecules two, three,
to the lungs where they grab onto oxygen molecules, and four is much easier.
100%
90%
1 Oxygen Released
Percent Oxygen Saturation of Hemoglobin
st
80%
70%
2 Oxygen Released
nd
60%
50%
Figure 2.1 The
hemoglobin
40%
3 Oxygen Released dissociation curve.
rd
Notice the extra-steep
30% slope in the middle of
the curve. This is the
reason for the cascade
20%
of oxygen binding (in
4 Oxygen Released the lungs) or oxygen
th
10%
release (in the distal
parts of the circulatory
0% system). Laser therapy
0 20 40 60 80 100 can trigger this release
mechanism in a
Partial Oxygen Pressure (mm Hg) localized way.
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 12 08/08/2019 09:46