Page 44 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 44
30 Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
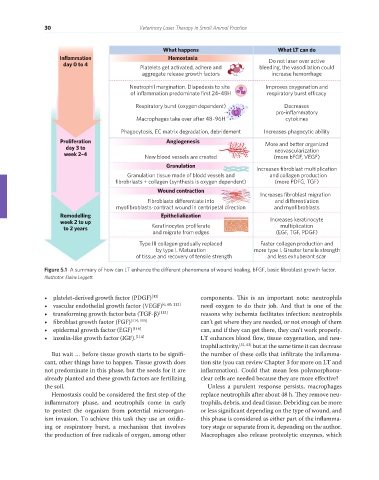
What happens What LT can do
Inflammation Hemostasia Do not laser over active
day 0 to 4
Platelets get activated, adhere and bleeding, the vasodilation could
aggregate release growth factors increase hemorrhage
Neutrophil margination. Diapedesis to site Improves oxygenation and
of inflammation predominate first 24–48H respiratory burst e cacy
Respiratory burst (oxygen dependent) Decreases
pro-inflammatory
Macrophages take over after 48–96H cytokines
Phagocytosis, EC matrix degradation, debridement Increases phagocytic ability
Proliferation Angiogenesis More and better organized
day 3 to neovascularization
week 2–4 New blood vessels are created (more bFGF, VEGF)
Granulation Increases fibroblast multiplication
Granulation tissue made of blodd vessels and and collagen production
fibrobrlasts + collagen (synthesis is oxygen dependent) (more PDFG, TGF)
Wound contraction
Increases fibroblast migration
Fibroblasts dierentiate into and dierentiation
myofibroblasts-contract wound in centripetal direction and myofibroblasts
Remodelling Epithelialization
week 2 to up Increases keratinocyte
to 2 years Keratinocytes proliferate multiplication
and migrate from edges (EGF, TGF, PDGF)
Type III collagen gradually replaced Faster collagen production and
by type I. Maturation more type I. Greater tensile strength
of tissue and recovery of tensile strength and less exhuberant scar
Figure 5.1 A summary of how can LT enhance the different phenomena of wound healing. bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor.
Illustrator: Elaine Leggett.
• platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) [43] components. This is an important note: neutrophils
• vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [6, 60, 112] need oxygen to do their job. And that is one of the
• transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) [113] reasons why ischemia facilitates infection: neutrophils
• fibroblast growth factor (FGF) [114, 115] can’t get where they are needed, or not enough of them
• epidermal growth factor (EGF) [116] can, and if they can get there, they can’t work properly.
• insulin-like growth factor (IGF). [114] LT enhances blood flow, tissue oxygenation, and neu-
trophil activity, [51, 52] but at the same time it can decrease
But wait … before tissue growth starts to be signifi- the number of these cells that infiltrate the inflamma-
cant, other things have to happen. Tissue growth does tion site (you can review Chapter 3 for more on LT and
not predominate in this phase, but the seeds for it are inflammation). Could that mean less polymorphonu-
already planted and these growth factors are fertilizing clear cells are needed because they are more effective?
the soil. Unless a purulent response persists, macrophages
Hemostasis could be considered the first step of the replace neutrophils after about 48 h. They remove neu-
inflammatory phase, and neutrophils come in early trophils, debris, and dead tissue. Debriding can be more
to protect the organism from potential microorgan- or less significant depending on the type of wound, and
ism invasion. To achieve this task they use an oxidiz- this phase is considered as either part of the inflamma-
ing or respiratory burst, a mechanism that involves tory stage or separate from it, depending on the author.
the production of free radicals of oxygen, among other Macrophages also release proteolytic enzymes, which
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 30 08/08/2019 09:47