Page 98 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 98
84 Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
Case no. 1
N., canine, 6 years old, Maltese, FS, 4 kg
• Complaint: chronic bilateral otitis.
• History: N. had been adopted 2 years before with a pre-existing otitis and the condition had never resolved.
Oral and topical treatments had been used with no result. Last culture was positive for Pseudomonas,
antibiogram showed sensitivity to marbofloxacin but again there was no response to oral and topical
treatment. Both tympanic membranes have been lost and MRI suggested both bullas are affected; owners
refused surgical treatment.
• Physical examination: severe bilateral otitis, with thick dark secretion, but without significant stenosis of
external ear canal.
• Diagnosis: chronic bilateral external and middle ear otitis due to Pseudomonas.
• Treatment:
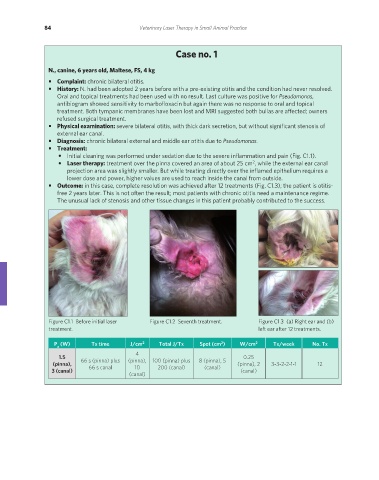
• Initial cleaning was performed under sedation due to the severe inflammation and pain (Fig. C1.1).
2
• Laser therapy: treatment over the pinna covered an area of about 25 cm , while the external ear canal
projection area was slightly smaller. But while treating directly over the inflamed epithelium requires a
lower dose and power, higher values are used to reach inside the canal from outside.
• Outcome: in this case, complete resolution was achieved after 12 treatments (Fig. C1.3); the patient is otitis-
free 2 years later. This is not often the result; most patients with chronic otitis need a maintenance regime.
The unusual lack of stenosis and other tissue changes in this patient probably contributed to the success.
Figure C1.1 Before initial laser Figure C1.2 Seventh treatment. Figure C1.3 (a) Right ear and (b)
treatment. left ear after 12 treatments.
2
P (W) Tx time J/cm 2 Total J/Tx Spot (cm ) W/cm 2 Tx/week No. Tx
a
4
1.5 0.25
(pinna), 66 s (pinna) plus (pinna), 100 (pinna) plus 8 (pinna), 5 (pinna), 2 3-3-2-2-1-1 12
3 (canal) 66 s canal 10 200 (canal) (canal) (canal)
(canal)
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 84 08/08/2019 09:47