Page 163 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 163
Blood and haemopoiesis (sanguis et haemocytopoesis) 145
azurophilic granules, vesicles, microtubules and microfila- The hyalomere (Figure 7.16) incorporates a system
VetBooks.ir ments. These cytoplasmic components become separated of vesicles and canaliculi that are formed by invagination
off and undergo fragmentation. The membrane-bound of the plasmalemma. Microtubules and actin and myo-
sin filaments form a network that maintains the shape of
fragmentation products constitute the platelets. The dura-
tion of platelet formation is considered to be 12 days. the platelet and enables contraction. The external surface
Morphological changes associated with thrombopoiesis of the cell membrane is covered with a glycocalyx. This
include: incorporates fibrinogen and thromboplastin, which are
important for formation of the platelet plug and adhe-
· increase in cell volume, sion of platelets to the vascular endothelium.
· reduction in basophilia and
· appearance of azurophilic granules. Blood clot formation
When a vessel wall is damaged, thrombocytes bind to col-
Platelet structure and function lagen fibres in the endothelium that are not exposed under
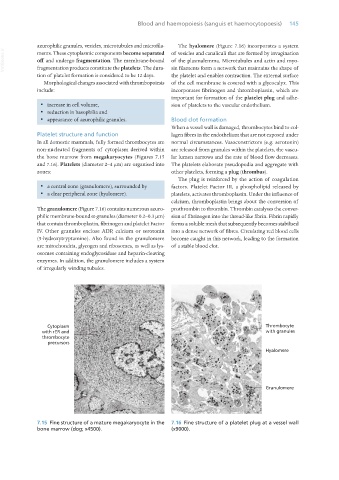
In all domestic mammals, fully formed thrombocytes are normal circumstances. Vasoconstrictors (e.g. serotonin)
non-nucleated fragments of cytoplasm derived within are released from granules within the platelets, the vascu-
the bone marrow from megakaryocytes (Figures 7.15 lar lumen narrows and the rate of blood flow decreases.
and 7.16). Platelets (diameter 2–4 μm) are organised into The platelets elaborate pseudopodia and aggregate with
zones: other platelets, forming a plug (thrombus).
The plug is reinforced by the action of coagulation
· a central zone (granulomere), surrounded by factors. Platelet Factor III, a phospholipid released by
· a clear peripheral zone (hyalomere). platelets, activates thromboplastin. Under the influence of
calcium, thromboplastin brings about the conversion of
The granulomere (Figure 7.16) contains numerous azuro- prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin catalyses the conver-
philic membrane-bound α-granules (diameter 0.2–0.3 μm) sion of fibrinogen into the thread-like fibrin. Fibrin rapidly
that contain thromboplastin, fibrinogen and platelet Factor forms a soluble mesh that subsequently becomes stabilised
IV. Other granules enclose ADP, calcium or serotonin into a dense network of fibres. Circulating red blood cells
(5-hydroxytryptamine). Also found in the granulomere become caught in this network, leading to the formation
are mitochondria, glycogen and ribosomes, as well as lys- of a stable blood clot.
osomes containing endoglycosidase and heparin-cleaving
enzymes. In addition, the granulomere includes a system
of irregularly winding tubules.
7.15 Fine structure of a mature megakaryocyte in the 7.16 Fine structure of a platelet plug at a vessel wall
bone marrow (dog; x4500). (x9000).
Vet Histology.indb 145 16/07/2019 14:58