Page 172 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 172
154 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
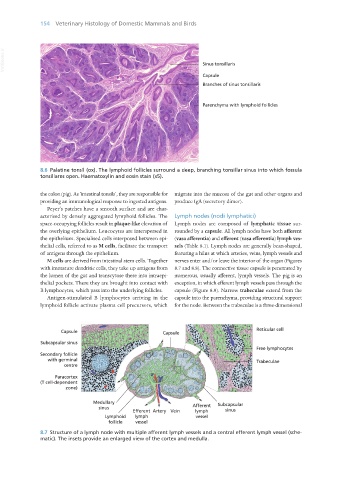
8.6 Palatine tonsil (ox). The lymphoid follicles surround a deep, branching tonsillar sinus into which fossula
tonsillares open. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x5).
the colon (pig). As ‘intestinal tonsils’, they are responsible for migrate into the mucosa of the gut and other organs and
providing an immunological response to ingested antigens. produce IgA (secretory dimer).
Peyer’s patches have a smooth surface and are char-
acterised by densely aggregated lymphoid follicles. The Lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici)
space-occupying follicles result in plaque-like elevation of Lymph nodes are composed of lymphatic tissue sur-
the overlying epithelium. Leucocytes are interspersed in rounded by a capsule. All lymph nodes have both afferent
the epithelium. Specialised cells interposed between epi- (vasa afferentia) and efferent (vasa efferentia) lymph ves-
thelial cells, referred to as M cells, facilitate the transport sels (Table 8.1). Lymph nodes are generally bean-shaped,
of antigens through the epithelium. featuring a hilus at which arteries, veins, lymph vessels and
M cells are derived from intestinal stem cells. Together nerves enter and/or leave the interior of the organ (Figures
with immature dendritic cells, they take up antigens from 8.7 and 8.8). The connective tissue capsule is penetrated by
the lumen of the gut and transcytose these into intraepi- numerous, usually afferent, lymph vessels. The pig is an
thelial pockets. There they are brought into contact with exception, in which efferent lymph vessels pass through the
B lymphocytes, which pass into the underlying follicles. capsule (Figure 8.9). Narrow trabeculae extend from the
Antigen-stimulated B lymphocytes arriving in the capsule into the parenchyma, providing structural support
lymphoid follicle activate plasma cell precursors, which for the node. Between the trabeculae is a three-dimensional
8.7 Structure of a lymph node with multiple afferent lymph vessels and a central efferent lymph vessel (sche-
matic). The insets provide an enlarged view of the cortex and medulla.
Vet Histology.indb 154 16/07/2019 14:59