Page 169 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 169
Immune system and lymphatic organs (organa Iymphopoetica) 151
thymic anlage is seeded with lymphocytes originating mature (naïve) T lymphocytes (T cells). In this process, T
VetBooks.ir from haemopoietic organs (liver, spleen, later bone mar- cells attain the capacity to distinguish between ‘self’ and
row). These cells accumulate primarily in the periphery of ‘non-self’. They acquire immunocompetence, developing
the thymus. The thymus thus becomes a lymphoepithelial the capacity to initiate an immune response upon contact
organ (Table 8.1). with an appropriately presented antigen.
The central function of the thymus is the differentia- The thymus is divided into lobes and incompletely
tion of lymphocytes arriving from the bone marrow into separated lobules (Figures 8.3 and 8.4). Each lobule is com-
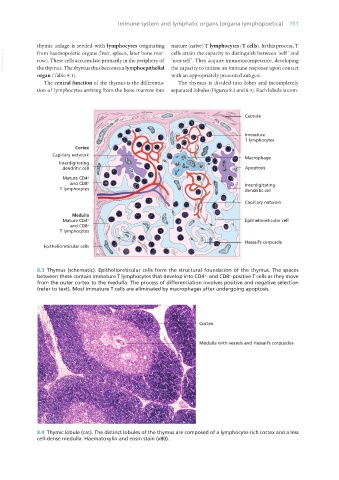
Capsule
Immature
T lymphocytes
Cortex
Capillary network
Macrophage
Interdigitating
dendritic cell Apoptosis
Mature CD4 +
and CD8 + Interdigitating
T lymphocytes dendritic cell
Capillary network
Medulla
Mature CD4 + Epithelioreticular cell
and CD8 +
T lymphocytes
Hassall’s corpuscle
Epithelioreticular cells
8.3 Thymus (schematic). Epithelioreticular cells form the structural foundation of the thymus. The spaces
between these contain immature T lymphocytes that develop into CD4 - and CD8 -positive T cells as they move
+
+
from the outer cortex to the medulla. The process of differentiation involves positive and negative selection
(refer to text). Most immature T cells are eliminated by macrophages after undergoing apoptosis.
8.4 Thymic lobule (cat). The distinct lobules of the thymus are composed of a lymphocyte-rich cortex and a less
cell-dense medulla. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x80).
Vet Histology.indb 151 16/07/2019 14:59