Page 208 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 208
190 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
of the secretory epithelial cells. The product of the glan-
· parotid salivary gland (glandula parotis),
VetBooks.ir · mandibular salivary gland (glandula mandibularis), dular epithelial cells passes into a system of ducts lined
by cuboidal to columnar epithelium. Structural features
· sublingual glands (glandulae sublinguales):
common to the major salivary glands include:
− glandula sublingualis monostomatica and
− glandula sublingualis polystomatica.
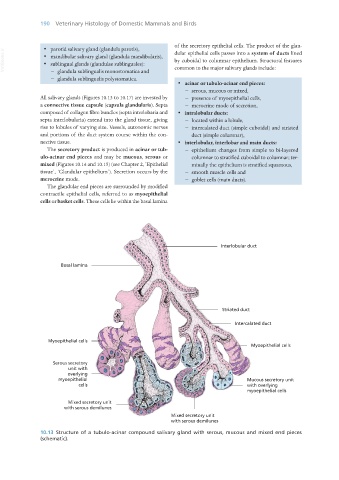
· acinar or tubulo-acinar end pieces:
− serous, mucous or mixed,
All salivary glands (Figures 10.13 to 10.17) are invested by − presence of myoepithelial cells,
a connective tissue capsule (capsula glandularis). Septa − merocrine mode of secretion,
composed of collagen fibre bundles (septa interlobaria and · intralobular ducts:
septa interlobularia) extend into the gland tissue, giving − located within a lobule,
rise to lobules of varying size. Vessels, autonomic nerves − intercalated duct (simple cuboidal) and striated
and portions of the duct system course within the con- duct (simple columnar),
nective tissue. · interlobular, interlobar and main ducts:
The secretory product is produced in acinar or tub- − epithelium changes from simple to bi-layered
ulo-acinar end pieces and may be mucous, serous or columnar to stratified cuboidal to columnar; ter-
mixed (Figures 10.14 and 10.15) (see Chapter 2, ‘Epithelial minally the epithelium is stratified squamous,
tissue’, ‘Glandular epithelium’). Secretion occurs by the − smooth muscle cells and
merocrine mode. − goblet cells (main ducts).
The glandular end pieces are surrounded by modified
contractile epithelial cells, referred to as myoepithelial
cells or basket cells. These cells lie within the basal lamina
10.13 Structure of a tubulo-acinar compound salivary gland with serous, mucous and mixed end pieces
(schematic).
Vet Histology-01-cnew.indd 190 06/08/2019 10:26