Page 211 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 211
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 193
VetBooks.ir
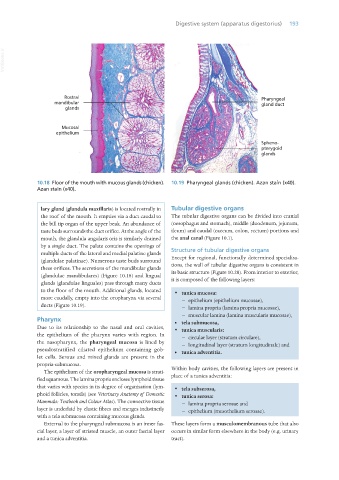
10.18 Floor of the mouth with mucous glands (chicken). 10.19 Pharyngeal glands (chicken). Azan stain (x40).
Azan stain (x40).
lary gland (glandula maxillaris) is located rostrally in Tubular digestive organs
the roof of the mouth. It empties via a duct caudal to The tubular digestive organs can be divided into cranial
the bill tip organ of the upper beak. An abundance of (oesophagus and stomach), middle (duodenum, jejunum,
taste buds surrounds the duct orifice. At the angle of the ileum) and caudal (caecum, colon, rectum) portions and
mouth, the glandula angularis oris is similarly drained the anal canal (Figure 10.1).
by a single duct. The palate contains the openings of
multiple ducts of the lateral and medial palatine glands Structure of tubular digestive organs
(glandulae palatinae). Numerous taste buds surround Except for regional, functionally determined specialisa-
these orifices. The secretions of the mandibular glands tions, the wall of tubular digestive organs is consistent in
(glandulae mandibulares) (Figure 10.18) and lingual its basic structure (Figure 10.20). From interior to exterior,
glands (glandulae linguales) pass through many ducts it is composed of the following layers:
to the floor of the mouth. Additional glands, located · tunica mucosa:
more caudally, empty into the oropharynx via several − epithelium (epithelium mucosae),
ducts (Figure 10.19).
− lamina propria (lamina propria mucosae),
− muscular lamina (lamina muscularis mucosae),
Pharynx • tela submucosa,
Due to its relationship to the nasal and oral cavities, · tunica muscularis:
the epithelium of the pharynx varies with region. In − circular layer (stratum circulare),
the nasopharynx, the pharyngeal mucosa is lined by − longitudinal layer (stratum longitudinale) and
pseudostratified ciliated epithelium containing gob- • tunica adventitia.
let cells. Serous and mixed glands are present in the
propria-submucosa.
The epithelium of the oropharyngeal mucosa is strati- Within body cavities, the following layers are present in
fied squamous. The lamina propria encloses lymphoid tissue place of a tunica adventitia:
that varies with species in its degree of organisation (lym- · tela subserosa,
phoid follicles, tonsils) (see Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic · tunica serosa:
Mammals: Textbook and Colour Atlas). The connective tissue − lamina propria serosae and
layer is underlaid by elastic fibres and merges indistinctly − epithelium (mesothelium serosae).
with a tela submucosa containing mucous glands.
External to the pharyngeal submucosa is an inner fas- These layers form a musculomembranous tube that also
cial layer, a layer of striated muscle, an outer fascial layer occurs in similar form elsewhere in the body (e.g. urinary
and a tunica adventitia. tract).
Vet Histology.indb 193 16/07/2019 15:00