Page 215 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 215
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 197
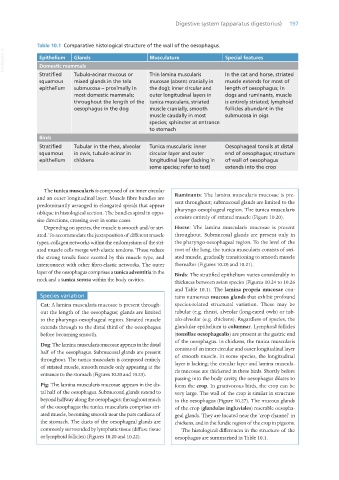
Table 10.1 Comparative histological structure of the wall of the oesophagus.
VetBooks.ir Epithelium Glands Musculature Special features
Domestic mammals
Stratified Tubulo-acinar mucous or Thin lamina muscularis In the cat and horse, striated
squamous mixed glands in the tela mucosae (absent cranially in muscle extends for most of
epithelium submucosa – proximally in the dog); inner circular and length of oesophagus; in
most domestic mammals; outer longitudinal layers in dogs and ruminants, muscle
throughout the length of the tunica muscularis, striated is entirely striated; lymphoid
oesophagus in the dog muscle cranially, smooth follicles abundant in the
muscle caudally in most submucosa in pigs
species; sphincter at entrance
to stomach
Birds
Stratified Tubular in the rhea, alveolar Tunica muscularis: inner Oesophageal tonsils at distal
squamous in owls, tubulo-acinar in circular layer and outer end of oesophagus; structure
epithelium chickens longitudinal layer (lacking in of wall of oesophagus
some species; refer to text) extends into the crop
The tunica muscularis is composed of an inner circular
and an outer longitudinal layer. Muscle fibre bundles are Ruminants: The lamina muscularis mucosae is pre-
predominantly arranged in elongated spirals that appear sent throughout; submucosal glands are limited to the
oblique in histological section. The bundles spiral in oppo- pharyngo-oesophageal region. The tunica muscularis
site directions, crossing over in some cases. consists entirely of striated muscle (Figure 10.20).
Depending on species, the muscle is smooth and/or stri- Horse: The lamina muscularis mucosae is present
ated. To accommodate the juxtaposition of different muscle throughout. Submucosal glands are present only in
types, collagen networks within the endomysium of the stri- the pharyngo-oesophageal region. To the level of the
ated muscle cells merge with elastic tendons. These reduce root of the lung, the tunica muscularis consists of stri-
the strong tensile force exerted by this muscle type, and ated muscle, gradually transitioning to smooth muscle
interconnect with other fibro-elastic networks. The outer thereafter (Figures 10.20 and 10.21).
layer of the oesophagus comprises a tunica adventitia in the Birds: The stratified epithelium varies considerably in
neck and a tunica serosa within the body cavities.
thickness between avian species (Figures 10.24 to 10.26
and Table 10.1). The lamina propria mucosae con-
Species variation tains numerous mucous glands that exhibit profound
Cat: A lamina muscularis mucosae is present through- species-related structural variation. These may be
out the length of the oesophagus; glands are limited tubular (e.g. rheas), alveolar (long-eared owls) or tub-
to the pharyngo-oesophageal region. Striated muscle ulo-alveolar (e.g. chickens). Regardless of species, the
extends through to the distal third of the oesophagus glandular epithelium is columnar. Lymphoid follicles
before becoming smooth. (tonsillae oesophagealis) are present at the gastric end
of the oesophagus. In chickens, the tunica muscularis
Dog: The lamina muscularis mucosae appears in the distal
half of the oesophagus. Submucosal glands are present consists of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer
throughout. The tunica muscularis is composed entirely of smooth muscle. In some species, the longitudinal
of striated muscle, smooth muscle only appearing at the layer is lacking; the circular layer and lamina muscula-
entrance to the stomach (Figures 10.20 and 10.23). ris mucosae are thickened in these birds. Shortly before
passing into the body cavity, the oesophagus dilates to
Pig: The lamina muscularis mucosae appears in the dis- form the crop. In granivorous birds, the crop can be
tal half of the oesophagus. Submucosal glands extend to very large. The wall of the crop is similar in structure
beyond halfway along the oesophagus; throughout much to the oesophagus (Figure 10.27). The mucous glands
of the oesophagus the tunica muscularis comprises stri- of the crop (glandulae ingluviales) resemble oesopha-
ated muscle, becoming smooth near the pars cardiaca of geal glands. They are located near the ‘crop channel’ in
the stomach. The ducts of the oesophageal glands are chickens, and in the fundic region of the crop in pigeons.
commonly surrounded by lymphatic tissue (diffuse tissue The histological differences in the structure of the
or lymphoid follicles) (Figures 10.20 and 10.22). oesophagus are summarised in Table 10.1.
Vet Histology.indb 197 16/07/2019 15:00