Page 218 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 218
200 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
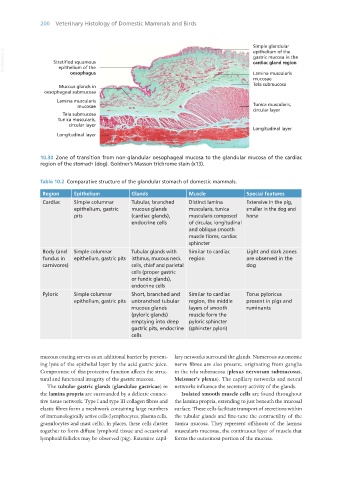
10.30 Zone of transition from non-glandular oesophageal mucosa to the glandular mucosa of the cardiac
region of the stomach (dog). Goldner’s Masson trichrome stain (x13).
Table 10.2 Comparative structure of the glandular stomach of domestic mammals.
Region Epithelium Glands Muscle Special features
Cardiac Simple columnar Tubular, branched Distinct lamina Extensive in the pig,
epithelium, gastric mucous glands muscularis, tunica smaller in the dog and
pits (cardiac glands), muscularis composed horse
endocrine cells of circular, longitudinal
and oblique smooth
muscle fibres, cardiac
sphincter
Body (and Simple columnar Tubular glands with Similar to cardiac Light and dark zones
fundus in epithelium, gastric pits isthmus, mucous neck region are observed in the
carnivores) cells, chief and parietal dog
cells (proper gastric
or fundic glands),
endocrine cells
Pyloric Simple columnar Short, branched and Similar to cardiac Torus pyloricus
epithelium, gastric pits unbranched tubular region, the middle present in pigs and
mucous glands layers of smooth ruminants
(pyloric glands) muscle form the
emptying into deep pyloric sphincter
gastric pits, endocrine (sphincter pylori)
cells
mucous coating serves as an additional barrier by prevent- lary networks surround the glands. Numerous autonomic
ing lysis of the epithelial layer by the acid gastric juice. nerve fibres are also present, originating from ganglia
Compromise of this protective function affects the struc- in the tela submucosa (plexus nervorum submucosus,
tural and functional integrity of the gastric mucosa. Meissner’s plexus). The capillary networks and neural
The tubular gastric glands (glandulae gastricae) in networks influence the secretory activity of the glands.
the lamina propria are surrounded by a delicate connec- Isolated smooth muscle cells are found throughout
tive tissue network. Type I and type III collagen fibres and the lamina propria, extending to just beneath the mucosal
elastic fibres form a meshwork containing large numbers surface. These cells facilitate transport of secretions within
of immunologically active cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells, the tubular glands and fine-tune the contractility of the
granulocytes and mast cells). In places, these cells cluster tunica mucosa. They represent offshoots of the lamina
together to form diffuse lymphoid tissue and occasional muscularis mucosae, the continuous layer of muscle that
lymphoid follicles may be observed (pig). Extensive capil- forms the outermost portion of the mucosa.
Vet Histology.indb 200 16/07/2019 15:01