Page 210 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 210
192 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
and energy-producing mitochondria facilitates absorption that these serous cells are in the same row as mucous cells,
VetBooks.ir of water and sodium ions, and excretion of potassium and that the ‘demilune’ shape is a fixation artefact. Mucus-
into the duct lumen. Capillary networks surrounding the secreting cells have a foamy basophilic cytoplasm and a
striated ducts participate in the reabsorption of fluid and basal nucleus. The lumen is relatively large. Mucous glands
ions from the saliva. Striated ducts thus serve to thicken contain fewer intercalated ducts and striated ducts, as
the saliva and regulate its electrolyte content. mucus does not undergo modification in the duct system.
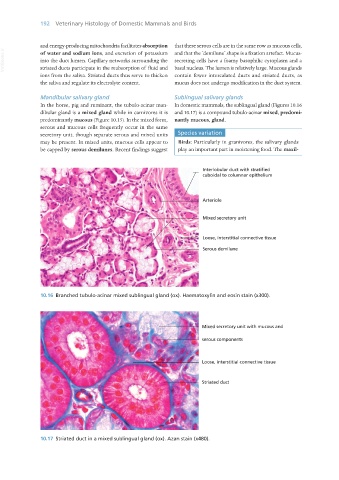
Mandibular salivary gland Sublingual salivary glands
In the horse, pig and ruminant, the tubulo-acinar man- In domestic mammals, the sublingual gland (Figures 10.16
dibular gland is a mixed gland while in carnivores it is and 10.17) is a compound tubulo-acinar mixed, predomi-
predominantly mucous (Figure 10.15). In the mixed form, nantly mucous, gland.
serous and mucous cells frequently occur in the same
secretory unit, though separate serous and mixed units Species variation
may be present. In mixed units, mucous cells appear to Birds: Particularly in granivores, the salivary glands
be capped by serous demilunes. Recent findings suggest play an important part in moistening food. The maxil-
10.16 Branched tubulo-acinar mixed sublingual gland (ox). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x300).
10.17 Striated duct in a mixed sublingual gland (ox). Azan stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 192 16/07/2019 15:00