Page 281 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 281
Urinary system (organa urinaria) 263
corpuscle (corpusculum renale) (Figures 12.9 to 12.12). The cortex is composed of the pars radiata (medullary
VetBooks.ir The nephron becomes elongated and convoluted, develop- rays), comprising straight segments of the proximal and
ing a descending and ascending limb, and joins the tubuli distal tubules as well as collecting ducts, and the pars con-
of the extensively branched derivatives of the ureteric bud. voluta (cortical labyrinth), containing renal corpuscles,
The latter differentiate to form the collecting duct system convoluted portions of the proximal and distal tubules and
that drains into the renal pelvis (and/or calyces) (refer to initial segments of the collecting duct system.
embryology textbooks for further detail). Nephrons can be The renal medulla contains ascending and descending
divided into two types: limbs of the loops of Henle, collecting ducts and papillary
ducts. The zona interna contains loops of Henle of long-
· cortical nephrons with short loops of Henle and looped nephrons, collecting ducts and the papillary ducts.
· juxtamedullary nephrons with long loops of Henle. The zona externa is composed largely of loops of Henle
of short-looped nephrons and collecting ducts.
Cortical nephrons are relatively short and extend only a
short distance into the renal medulla, generally as far as Species variation
the boundary between the internal and external medullary Variation is observed in the relative number of long-
zones (see below). and short-looped nephrons.
Juxtamedullary nephrons are particularly numerous Horse and small ruminants: Short-looped nephrons
in carnivores. Their long, thin loops extend deep into the predominate, with renal corpuscles located mainly in
medulla. The straight portion of the proximal tubule (see the outer cortex.
below) is continuous with the descending, thin limb of the
loop of Henle. Ox, pig, dog and cat: Most nephrons are long-looped,
Based on the size and number of renal corpuscles, the with the renal corpuscles located closer to the medulla
arrangement of proximal and distal tubules, the length of (juxtamedullary glomeruli).
the loop of Henle and the distribution of vessels, the renal
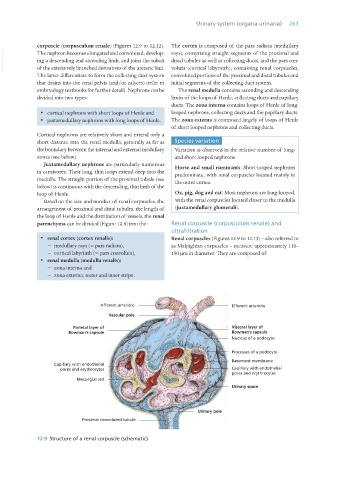
parenchyma can be divided (Figure 12.8) into the: Renal corpuscle (corpusculum renale) and
ultrafiltration
· renal cortex (cortex renalis): Renal corpuscles (Figures 12.9 to 12.13) – also referred to
− medullary rays (= pars radiata), as Malpighian corpuscles – measure approximately 110–
− cortical labyrinth (= pars convoluta), 150 μm in diameter. They are composed of:
· renal medulla (medulla renalis):
− zona interna and
− zona externa; outer and inner stripe.
12.9 Structure of a renal corpuscle (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 263 16/07/2019 15:03