Page 32 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 32
14 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
apparatus in a similar manner. The cis side thus represents Membrane recycling: Fusion of the transport vesicle
VetBooks.ir the side of substance uptake and growth of the dictyosome. membrane with the plasmalemma results in an increase
Trans side: The trans side features an accumulation in the surface area of the cell. This phenomenon is limited
of vesicles that are still in contact with, or have become by the simultaneous invagination and incorporation of
detached from, the membrane. The proteins in these vesi- segments of the plasmalemma into the cytoplasm where
cles are destined for various locations including the apical they are utilised in forming membranes of new transport
cytoplasm (secretory proteins within secretory vesicles) vesicles.
and lysosomes (membrane proteins and enzymes). This
side of the Golgi apparatus is thus responsible for sorting Organelles of cellular respiration and energy
and vesicle distribution. production
Function: The primary function of the Golgi appa- The viability of a cell is sustained by metabolically active
ratus is terminal processing of macromolecules and cellular organelles and by intracellular transport of solid
targeted dispersal of the resulting end products to their and dissolved substances. To support these processes, the
final destination. Proteins synthesised in the ER are glyco- cell requires endogenous sources of energy. This is the role
sylated (with complex oligosaccharides and mannose-rich of the mitochondria.
oligosaccharides) to form glycoproteins, proteoglycans
and lysosomal proteins. Modification of lipoproteins also MITOCHONDRIA
occurs in the Golgi apparatus. Mitochondria supply energy to the cell through two main
In actively secreting cells, the Golgi apparatus serves to mechanisms:
create a stockpile of cellular secretions. The concentra-
tion of secretory product allows for rapid release from the · energy release through cellular respiration (oxida-
cell in response to increased demand. The Golgi apparatus tive phosphorylation) and
therefore assumes cell-specific roles in storage, transport · synthesis of specialised metabolic enzymes.
and release of secretions.
Secretory vesicles leave the trans side of the Golgi In a multi-stage process, culminating in oxidative phos-
apparatus and travel, generally via a system of micro- phorylation, mitochondria break down sugars and fatty
tubules or microfilaments, to the cell surface. There, acids to form CO and H O. This process is accompanied
2 2
the outer membrane of the transport vesicle fuses with by the liberation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a
the plasmalemma and its contents are transferred into the molecule containing stored energy. Mitochondria also par-
extracellular environment (exocytosis). Secretion may be ticipate in other processes associated with metabolism e.g.
regulated by neurotransmitters (e.g. acetylcholine) or by components of lipogenesis, the urea cycle and gluconeo-
hormones (e.g. cholecystokinin in the pancreas). genesis. Structurally, mitochondria are differentiated into
Other vesicles are delivered to the apical and basolateral a number of compartments (see below).
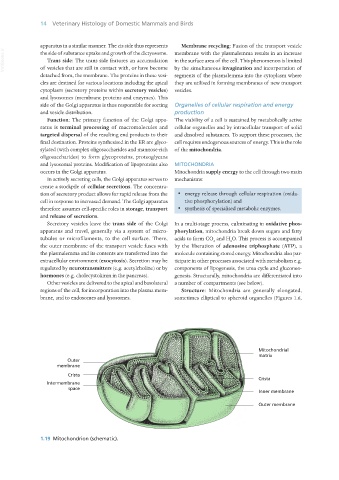
regions of the cell, for incorporation into the plasma mem- Structure: Mitochondria are generally elongated,
brane, and to endosomes and lysosomes. sometimes elliptical to spheroid organelles (Figures 1.6,
1.19 Mitochondrion (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 14 16/07/2019 14:53