Page 31 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 31
The cell (cellula) 13
Function: Smooth ER is abundant in cells that are GOLGI APPARATUS (COMPLEXUS GOLGIENSIS)
VetBooks.ir active in lipid metabolism (e.g. liver cells). The mem-
The Golgi apparatus is named after the Italian neurohistol-
brane of the sER contains enzymes involved in synthesis ogist and Nobel prize winner, Camillo Golgi (1843–1926).
of lipoproteins and serves as an anchor for components of With the aid of a similarly eponymous silver stain, Golgi
gluconeogenesis. In the liver, the sER contains enzymes observed what he described as an apparato reticulare interno
involved in detoxification (e.g. of harmful hydrocarbons). within nerve cells derived from the cerebellum.
Steroid hormone synthesis takes place in the smooth ER Structure: The Golgi apparatus is a compound struc-
of cells of the adrenal cortex and corpus luteum. Muscle ture composed of slightly curved clusters of stacked,
cells contain a modified form of sER (sarcoplasmic reticu- flattened (plate-like) membrane-bound cisternae or sacs.
2+
lum), in which Ca ions are stored. The membrane stacks have a smooth surface and are
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum also participates in the not in direct contact with one another. As in the endoplas-
formation and recycling of cellular membranes. mic reticulum, the membranes enclose a lumen that may
be dilated, depending on the activity of the cell. Dilatations
Organelles of protein modification and at the ends of the cisternae become pinched off to form
vesicular trafficking vesicles. Individual membrane stacks are also referred to
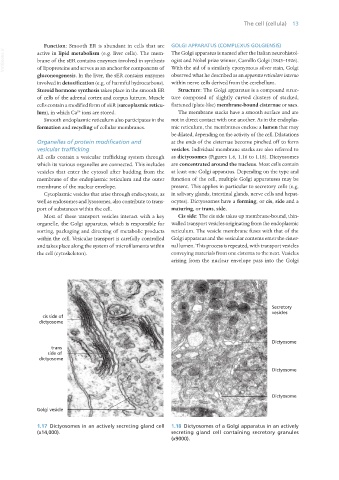
All cells contain a vesicular trafficking system through as dictyosomes (Figures 1.6, 1.16 to 1.18). Dictyosomes
which its various organelles are connected. This includes are concentrated around the nucleus. Most cells contain
vesicles that enter the cytosol after budding from the at least one Golgi apparatus. Depending on the type and
membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum and the outer function of the cell, multiple Golgi apparatuses may be
membrane of the nuclear envelope. present. This applies in particular to secretory cells (e.g.
Cytoplasmic vesicles that arise through endocytosis, as in salivary glands, intestinal glands, nerve cells and hepat-
well as endosomes and lysosomes, also contribute to trans- ocytes). Dictyosomes have a forming, or cis, side and a
port of substances within the cell. maturing, or trans, side.
Most of these transport vesicles interact with a key Cis side: The cis side takes up membrane-bound, thin-
organelle, the Golgi apparatus, which is responsible for walled transport vesicles originating from the endoplasmic
sorting, packaging and directing of metabolic products reticulum. The vesicle membrane fuses with that of the
within the cell. Vesicular transport is carefully controlled Golgi apparatus and the vesicular contents enter the cister-
and takes place along the system of microfilaments within nal lumen. This process is repeated, with transport vesicles
the cell (cytoskeleton). conveying materials from one cisterna to the next. Vesicles
arising from the nuclear envelope pass into the Golgi
1.17 Dictyosomes in an actively secreting gland cell 1.18 Dictyosomes of a Golgi apparatus in an actively
(x14,000). secreting gland cell containing secretory granules
(x9000).
Vet Histology.indb 13 16/07/2019 14:52