Page 34 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 34
16 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
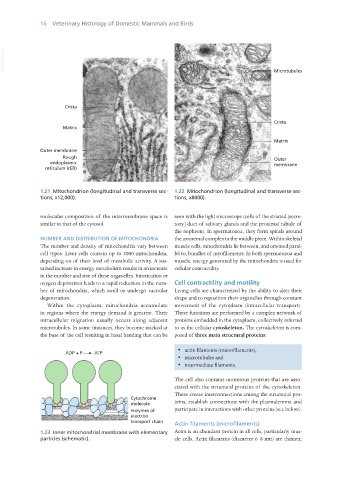
1.21 Mitochondrion (longitudinal and transverse sec- 1.22 Mitochondrion (longitudinal and transverse sec-
tions, x12,000). tions, x8000).
molecular composition of the intermembrane space is seen with the light microscope (cells of the striated [secre-
similar to that of the cytosol. tory] duct of salivary glands and the proximal tubule of
the nephron). In spermatozoa, they form spirals around
NUMBER AND DISTRIBUTION OF MITOCHONDRIA the axonemal complex in the middle piece. Within skeletal
The number and density of mitochondria vary between muscle cells, mitochondria lie between, and oriented paral-
cell types. Liver cells contain up to 3000 mitochondria, lel to, bundles of myofilaments. In both spermatozoa and
depending on of their level of metabolic activity. A sus- muscle, energy generated by the mitochondria is used for
tained increase in energy metabolism results in an increase cellular contractility.
in the number and size of these organelles. Intoxication or
oxygen deprivation leads to a rapid reduction in the num- Cell contractility and motility
ber of mitochondria, which swell or undergo vacuolar Living cells are characterised by the ability to alter their
degeneration. shape and to reposition their organelles through constant
Within the cytoplasm, mitochondria accumulate movement of the cytoplasm (intracellular transport).
in regions where the energy demand is greatest. Their These functions are performed by a complex network of
intracellular migration usually occurs along adjacent proteins embedded in the cytoplasm, collectively referred
microtubules. In some instances, they become stacked at to as the cellular cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is com-
the base of the cell resulting in basal banding that can be posed of three main structural proteins:
· actin filaments (microfilaments),
· microtubules and
· intermediate filaments.
The cell also contains numerous proteins that are asso-
ciated with the structural proteins of the cytoskeleton.
These create interconnections among the structural pro-
teins, establish connections with the plasmalemma and
participate in interactions with other proteins (see below).
Actin filaments (microfilaments)
1.23 Inner mitochondrial membrane with elementary Actin is an abundant protein in all cells, particularly mus-
particles (schematic). cle cells. Actin filaments (diameter 6–8 nm) are thinner,
Vet Histology.indb 16 16/07/2019 14:53