Page 38 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 38
20 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
disappears. The MTOC also coordinates the formation of Cilia and flagella are bounded by the plasmalemma.
VetBooks.ir new microtubules. The many proteins found in the peri- Both have the same structure and are distinguished by their
centriolar material of the MTOC include γ-tubulin, which length (cilia 2–10 μm, flagella up to 200 μm) (Figures 1.28
serves as the starting point for formation of new micro-
to 1.30).
tubules. The α- and β-tubulin dimers attach in a specific
orientation to the γ-tubulin molecules. Intermediate filaments
Intermediate filaments are polypeptide chains that provide
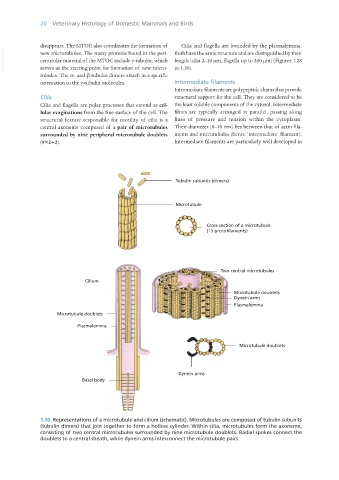
Cilia structural support for the cell. They are considered to be
Cilia and flagella are polar processes that extend as cel- the least soluble components of the cytosol. Intermediate
lular evaginations from the free surface of the cell. The fibres are typically arranged in parallel, passing along
structural feature responsible for motility of cilia is a lines of pressure and tension within the cytoplasm.
central axoneme composed of a pair of microtubules Their diameter (8–10 nm) lies between that of actin fila-
surrounded by nine peripheral microtubule doublets ments and microtubules (hence ‘intermediate’ filament).
(9×2+2). Intermediate filaments are particularly well developed in
Tubulin subunits (dimers)
Microtubule
Cross-section of a microtubule
(13 protofilaments)
Two central microtubules
Cilium
Microtubule doublets
Dynein arms
Plasmalemma
Microtubule doublets
Plasmalemma
Microtubule doublets
Dynein arms
Basal body
1.30 Representations of a microtubule and cilium (schematic). Microtubules are composed of tubulin subunits
(tubulin dimers) that join together to form a hollow cylinder. Within cilia, microtubules form the axoneme,
consisting of two central microtubules surrounded by nine microtubule doublets. Radial spokes connect the
doublets to a central sheath, while dynein arms interconnect the microtubule pairs.
Vet Histology.indb 20 16/07/2019 14:53