Page 1142 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1142
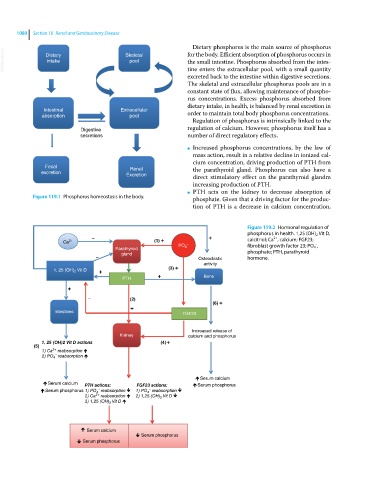
1080 Section 10 Renal and Genitourinary Disease
Dietary phosphorus is the main source of phosphorus
VetBooks.ir Dietary Skeletal for the body. Efficient absorption of phosphorus occurs in
the small intestine. Phosphorus absorbed from the intes
intake
pool
tine enters the extracellular pool, with a small quantity
excreted back to the intestine within digestive secretions.
The skeletal and extracellular phosphorus pools are in a
constant state of flux, allowing maintenance of phospho
rus concentrations. Excess phosphorus absorbed from
dietary intake, in health, is balanced by renal excretion in
Intestinal Extracellular
absorption pool order to maintain total body phosphorus concentrations.
Regulation of phosphorus is intrinsically linked to the
Digestive regulation of calcium. However, phosphorus itself has a
secretions number of direct regulatory effects.
Increased phosphorus concentrations, by the law of
●
mass action, result in a relative decline in ionized cal
cium concentration, driving production of PTH from
Fecal Renal the parathyroid gland. Phosphorus can also have a
excretion Excretion direct stimulatory effect on the parathyroid glandm
increasing production of PTH.
PTH acts on the kidney to decrease absorption of
●
Figure 119.1 Phosphorus homeostasis in the body. phosphate. Given that a driving factor for the produc
tion of PTH is a decrease in calcium concentration,
Figure 119.2 Hormonal regulation of
phosphorus in health. 1,25 (OH) 2 Vit D,
2+
– (1) + + calcitriol; Ca , calcium; FGF23;
Ca 2+ – fibroblast growth factor 23; PO 4 ,
‐
Parathyroid PO 4 phosphate; PTH, parathyroid
gland
– Osteoclastic hormone.
activity
(3) +
1, 25 (OH) 2 Vit D +
PTH + Bone
+
– (2)
(6) +
+
Intestines FGF23
Increased release of
Kidney calcium and phosphorus
1, 25 (OH)2 Vit D actions (4) +
(5)
PTH actions: FGF23 actions: