Page 301 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 301
306 18 Pleura
(a) (b)
(c)
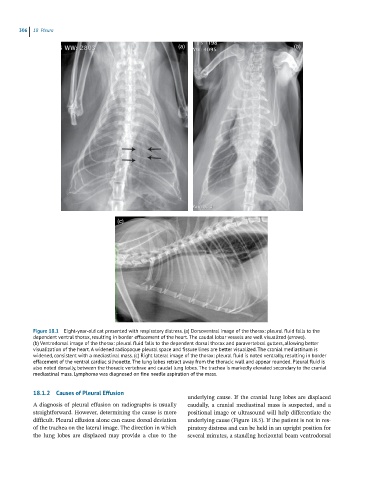
Figure 18.1 Eight-year-old cat presented with respiratory distress. (a) Dorsoventral image of the thorax: pleural fluid falls to the
dependent ventral thorax, resulting in border effacement of the heart. The caudal lobar vessels are well visualized (arrows).
(b) Ventrodorsal image of the thorax: pleural fluid falls to the dependent dorsal thorax and paravertebral gutters, allowing better
visualization of the heart. A widened radiopaque pleural space and fissure lines are better visualized. The cranial mediastinum is
widened, consistent with a mediastinal mass. (c) Right lateral image of the thorax: pleural fluid is noted ventrally, resulting in border
effacement of the ventral cardiac silhouette. The lung lobes retract away from the thoracic wall and appear rounded. Pleural fluid is
also noted dorsally, between the thoracic vertebrae and caudal lung lobes. The trachea is markedly elevated secondary to the cranial
mediastinal mass. Lymphoma was diagnosed on fine needle aspiration of the mass.
18.1.2 Causes of Pleural Effusion
underlying cause. If the cranial lung lobes are displaced
A diagnosis of pleural effusion on radiographs is usually caudally, a cranial mediastinal mass is suspected, and a
straightforward. However, determining the cause is more positional image or ultrasound will help differentiate the
difficult. Pleural effusion alone can cause dorsal deviation underlying cause (Figure 18.5). If the patient is not in res-
of the trachea on the lateral image. The direction in which piratory distress and can be held in an upright position for
the lung lobes are displaced may provide a clue to the several minutes, a standing horizontal beam ventrodorsal