Page 424 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 424
434 25 Adrenal Gland
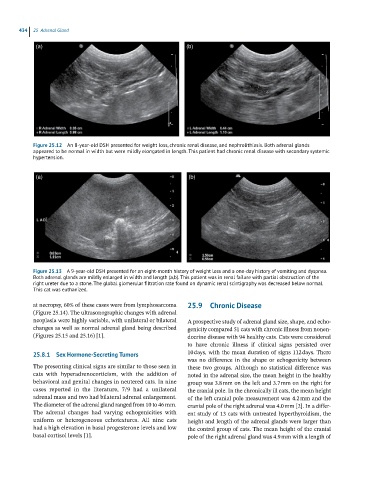
(a) (b)
Figure 25.12 An 8-year-old DSH presented for weight loss, chronic renal disease, and nephrolithiasis. Both adrenal glands
appeared to be normal in width but were mildly elongated in length. This patient had chronic renal disease with secondary systemic
hypertension.
(a) (b)
Figure 25.13 A 9-year-old DSH presented for an eight-month history of weight loss and a one-day history of vomiting and dyspnea.
Both adrenal glands are mildly enlarged in width and length (a,b). This patient was in renal failure with partial obstruction of the
right ureter due to a stone. The global glomerular filtration rate found on dynamic renal scintigraphy was decreased below normal.
This cat was euthanized.
at necropsy, 60% of these cases were from lymphosarcoma 25.9 Chronic Disease
(Figure 25.14). The ultrasonographic changes with adrenal
neoplasia were highly variable, with unilateral or bilateral A prospective study of adrenal gland size, shape, and echo-
changes as well as normal adrenal gland being described genicity compared 51 cats with chronic illness from nonen-
(Figures 25.15 and 25.16) [1]. docrine disease with 94 healthy cats. Cats were considered
to have chronic illness if clinical signs persisted over
25.8.1 Sex Hormone-Secreting Tumors 10 days, with the mean duration of signs 112 days. There
was no difference in the shape or echogenicity between
The presenting clinical signs are similar to those seen in these two groups. Although no statistical difference was
cats with hyperadrenocorticism, with the addition of noted in the adrenal size, the mean height in the healthy
behavioral and genital changes in neutered cats. In nine group was 3.8 mm on the left and 3.7 mm on the right for
cases reported in the literature, 7/9 had a unilateral the cranial pole. In the chronically ill cats, the mean height
adrenal mass and two had bilateral adrenal enlargement. of the left cranial pole measurement was 4.2 mm and the
The diameter of the adrenal gland ranged from 10 to 46 mm. cranial pole of the right adrenal was 4.0 mm [2]. In a differ-
The adrenal changes had varying echogenicities with ent study of 13 cats with untreated hyperthyroidism, the
uniform or heterogeneous echotextures. All nine cats height and length of the adrenal glands were larger than
had a high elevation in basal progesterone levels and low the control group of cats. The mean height of the cranial
basal cortisol levels [1]. pole of the right adrenal gland was 4.9 mm with a length of