Page 108 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 108
complement pathway then can proceed to completion and the
VetBooks.ir killing of the organism by terminal complement complexes.
The lectin pathway is ancient, having existed for at least 300
million years (It is present in many invertebrates (see Chapter 43).
Although in many ways it duplicates the alternative pathway, it is
an example of the way the body uses redundant mechanisms to
ensure protection.
The Classical Pathway
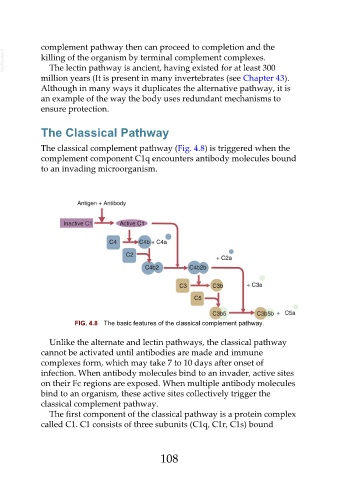
The classical complement pathway (Fig. 4.8) is triggered when the
complement component C1q encounters antibody molecules bound
to an invading microorganism.
FIG. 4.8 The basic features of the classical complement pathway.
Unlike the alternate and lectin pathways, the classical pathway
cannot be activated until antibodies are made and immune
complexes form, which may take 7 to 10 days after onset of
infection. When antibody molecules bind to an invader, active sites
on their Fc regions are exposed. When multiple antibody molecules
bind to an organism, these active sites collectively trigger the
classical complement pathway.
The first component of the classical pathway is a protein complex
called C1. C1 consists of three subunits (C1q, C1r, C1s) bound
108