Page 113 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 113
VetBooks.ir
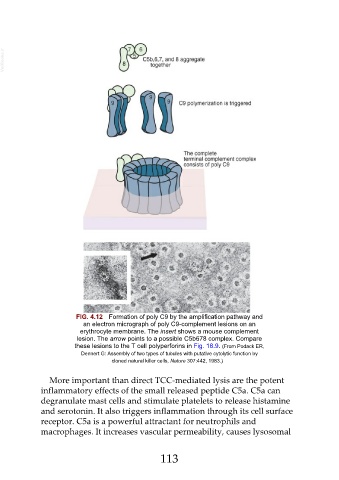
FIG. 4.12 Formation of poly C9 by the amplification pathway and
an electron micrograph of poly C9-complement lesions on an
erythrocyte membrane. The insert shows a mouse complement
lesion. The arrow points to a possible C5b678 complex. Compare
these lesions to the T cell polyperforins in Fig. 18.9. (From Podack ER,
Dennert G: Assembly of two types of tubules with putative cytolytic function by
cloned natural killer cells, Nature 307:442, 1983.)
More important than direct TCC-mediated lysis are the potent
inflammatory effects of the small released peptide C5a. C5a can
degranulate mast cells and stimulate platelets to release histamine
and serotonin. It also triggers inflammation through its cell surface
receptor. C5a is a powerful attractant for neutrophils and
macrophages. It increases vascular permeability, causes lysosomal
113