Page 449 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 449
VetBooks.ir
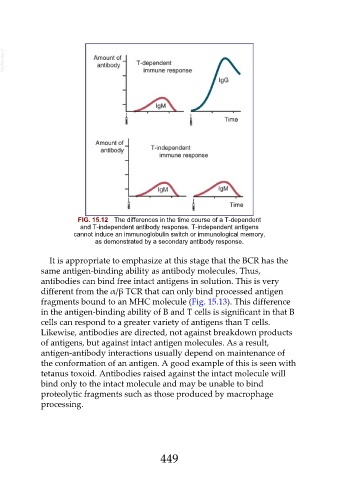
FIG. 15.12 The differences in the time course of a T-dependent
and T-independent antibody response. T-independent antigens
cannot induce an immunoglobulin switch or immunological memory,
as demonstrated by a secondary antibody response.
It is appropriate to emphasize at this stage that the BCR has the
same antigen-binding ability as antibody molecules. Thus,
antibodies can bind free intact antigens in solution. This is very
different from the α/β TCR that can only bind processed antigen
fragments bound to an MHC molecule (Fig. 15.13). This difference
in the antigen-binding ability of B and T cells is significant in that B
cells can respond to a greater variety of antigens than T cells.
Likewise, antibodies are directed, not against breakdown products
of antigens, but against intact antigen molecules. As a result,
antigen-antibody interactions usually depend on maintenance of
the conformation of an antigen. A good example of this is seen with
tetanus toxoid. Antibodies raised against the intact molecule will
bind only to the intact molecule and may be unable to bind
proteolytic fragments such as those produced by macrophage
processing.
449