Page 518 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 518
VetBooks.ir
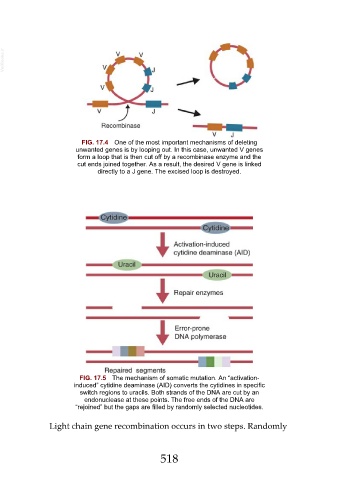
FIG. 17.4 One of the most important mechanisms of deleting
unwanted genes is by looping out. In this case, unwanted V genes
form a loop that is then cut off by a recombinase enzyme and the
cut ends joined together. As a result, the desired V gene is linked
directly to a J gene. The excised loop is destroyed.
FIG. 17.5 The mechanism of somatic mutation. An “activation-
induced” cytidine deaminase (AID) converts the cytidines in specific
switch regions to uracils. Both strands of the DNA are cut by an
endonuclease at these points. The free ends of the DNA are
“rejoined” but the gaps are filled by randomly selected nucleotides.
Light chain gene recombination occurs in two steps. Randomly
518