Page 572 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 572
VetBooks.ir
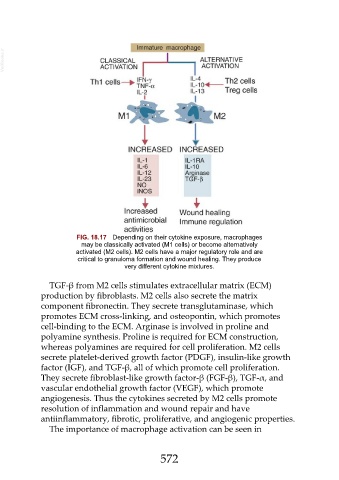
FIG. 18.17 Depending on their cytokine exposure, macrophages
may be classically activated (M1 cells) or become alternatively
activated (M2 cells). M2 cells have a major regulatory role and are
critical to granuloma formation and wound healing. They produce
very different cytokine mixtures.
TGF-β from M2 cells stimulates extracellular matrix (ECM)
production by fibroblasts. M2 cells also secrete the matrix
component fibronectin. They secrete transglutaminase, which
promotes ECM cross-linking, and osteopontin, which promotes
cell-binding to the ECM. Arginase is involved in proline and
polyamine synthesis. Proline is required for ECM construction,
whereas polyamines are required for cell proliferation. M2 cells
secrete platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), insulin-like growth
factor (IGF), and TGF-β, all of which promote cell proliferation.
They secrete fibroblast-like growth factor-β (FGF-β), TGF-α, and
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which promote
angiogenesis. Thus the cytokines secreted by M2 cells promote
resolution of inflammation and wound repair and have
antiinflammatory, fibrotic, proliferative, and angiogenic properties.
The importance of macrophage activation can be seen in
572