Page 132 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 132
114 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
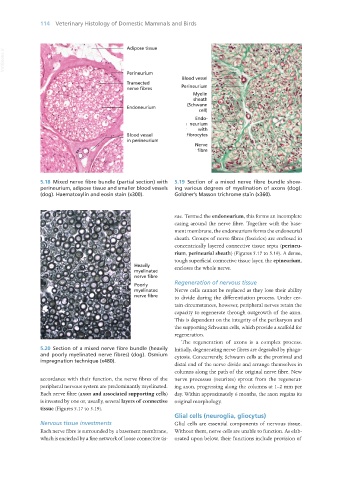
5.18 Mixed nerve fibre bundle (partial section) with 5.19 Section of a mixed nerve fibre bundle show-
perineurium, adipose tissue and smaller blood vessels ing various degrees of myelination of axons (dog).
(dog). Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x300). Goldner’s Masson trichrome stain (x360).
sue. Termed the endoneurium, this forms an incomplete
casing around the nerve fibre. Together with the base-
ment membrane, the endoneurium forms the endoneurial
sheath. Groups of nerve fibres (fascicles) are enclosed in
concentrically layered connective tissue septa (perineu-
rium, perineurial sheath) (Figures 5.17 to 5.19). A dense,
tough superficial connective tissue layer, the epineurium,
encloses the whole nerve.
Regeneration of nervous tissue
Nerve cells cannot be replaced as they lose their ability
to divide during the differentiation process. Under cer-
tain circumstances, however, peripheral nerves retain the
capacity to regenerate through outgrowth of the axon.
This is dependent on the integrity of the perikaryon and
the supporting Schwann cells, which provide a scaffold for
regeneration.
The regeneration of axons is a complex process.
5.20 Section of a mixed nerve fibre bundle (heavily Initially, degenerating nerve fibres are degraded by phago-
and poorly myelinated nerve fibres) (dog). Osmium cytosis. Concurrently, Schwann cells at the proximal and
impregnation technique (x480).
distal end of the nerve divide and arrange themselves in
columns along the path of the original nerve fibre. New
accordance with their function, the nerve fibres of the nerve processes (neurites) sprout from the regenerat-
peripheral nervous system are predominantly myelinated. ing axon, progressing along the columns at 1–2 mm per
Each nerve fibre (axon and associated supporting cells) day. Within approximately 6 months, the axon regains its
is invested by one or, usually, several layers of connective original morphology.
tissue (Figures 5.17 to 5.19).
Glial cells (neuroglia, gliocytus)
Nervous tissue investments Glial cells are essential components of nervous tissue.
Each nerve fibre is surrounded by a basement membrane, Without them, nerve cells are unable to function. As elab-
which is encircled by a fine network of loose connective tis- orated upon below, their functions include provision of
Vet Histology.indb 114 16/07/2019 14:57