Page 129 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 129
Nervous tissue (textus nervosus) 111
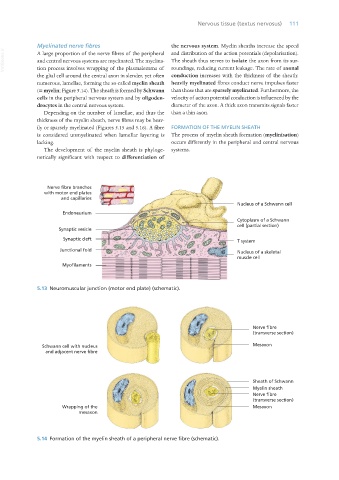
Myelinated nerve fibres the nervous system. Myelin sheaths increase the speed
VetBooks.ir A large proportion of the nerve fibres of the peripheral and distribution of the action potentials (depolarisation).
The sheath thus serves to isolate the axon from its sur-
and central nervous systems are myelinated. The myelina-
tion process involves wrapping of the plasmalemma of roundings, reducing current leakage. The rate of axonal
the glial cell around the central axon in slender, yet often conduction increases with the thickness of the sheath:
numerous, lamellae, forming the so-called myelin sheath heavily myelinated fibres conduct nerve impulses faster
(= myelin; Figure 5.14). The sheath is formed by Schwann than those that are sparsely myelinated. Furthermore, the
cells in the peripheral nervous system and by oligoden- velocity of action potential conduction is influenced by the
drocytes in the central nervous system. diameter of the axon. A thick axon transmits signals faster
Depending on the number of lamellae, and thus the than a thin axon.
thickness of the myelin sheath, nerve fibres may be heav-
ily or sparsely myelinated (Figures 5.15 and 5.16). A fibre FORMATION OF THE MYELIN SHEATH
is considered unmyelinated when lamellar layering is The process of myelin sheath formation (myelinisation)
lacking. occurs differently in the peripheral and central nervous
The development of the myelin sheath is phyloge- systems.
netically significant with respect to differentiation of
5.13 Neuromuscular junction (motor end plate) (schematic).
Nerve fibre
(transverse section)
Schwann cell with nucleus Mesaxon
and adjacent nerve fibre
Sheath of Schwann
Myelin sheath
Nerve fibre
(transverse section)
Wrapping of the Mesaxon
mesaxon
5.14 Formation of the myelin sheath of a peripheral nerve fibre (schematic).
Vet Histology.indb 111 16/07/2019 14:57