Page 124 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 124
106 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
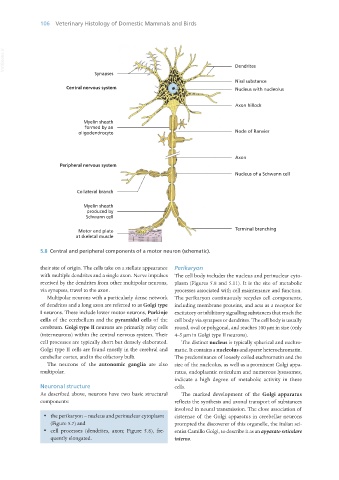
5.8 Central and peripheral components of a motor neuron (schematic).
their site of origin. The cells take on a stellate appearance Perikaryon
with multiple dendrites and a single axon. Nerve impulses The cell body includes the nucleus and perinuclear cyto-
received by the dendrites from other multipolar neurons, plasm (Figures 5.8 and 5.11). It is the site of metabolic
via synapses, travel to the axon. processes associated with cell maintenance and function.
Multipolar neurons with a particularly dense network The perikaryon continuously recycles cell components,
of dendrites and a long axon are referred to as Golgi type including membrane proteins, and acts as a receptor for
I neurons. These include lower motor neurons, Purkinje excitatory or inhibitory signalling substances that reach the
cells of the cerebellum and the pyramidal cells of the cell body via synapses or dendrites. The cell body is usually
cerebrum. Golgi type II neurons are primarily relay cells round, oval or polygonal, and reaches 100 μm in size (only
(interneurons) within the central nervous system. Their 4–5 μm in Golgi type II neurons).
cell processes are typically short but densely elaborated. The distinct nucleus is typically spherical and euchro-
Golgi type II cells are found mostly in the cerebral and matic. It contains a nucleolus and sparse heterochromatin.
cerebellar cortex, and in the olfactory bulb. The predominance of loosely coiled euchromatin and the
The neurons of the autonomic ganglia are also size of the nucleolus, as well as a prominent Golgi appa-
multipolar. ratus, endoplasmic reticulum and numerous lysosomes,
indicate a high degree of metabolic activity in these
Neuronal structure cells.
As described above, neurons have two basic structural The marked development of the Golgi apparatus
components: reflects the synthesis and axonal transport of substances
involved in neural transmission. The close association of
· the perikaryon – nucleus and perinuclear cytoplasm cisternae of the Golgi apparatus in cerebellar neurons
(Figure 5.7) and prompted the discoverer of this organelle, the Italian sci-
· cell processes (dendrites, axon; Figure 5.8), fre- entist Camillo Golgi, to describe it as an apparato reticulare
quently elongated. interno.
Vet Histology.indb 106 16/07/2019 14:57