Page 265 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 265
Respiratory system (apparatus respiratorius) 247
VetBooks.ir
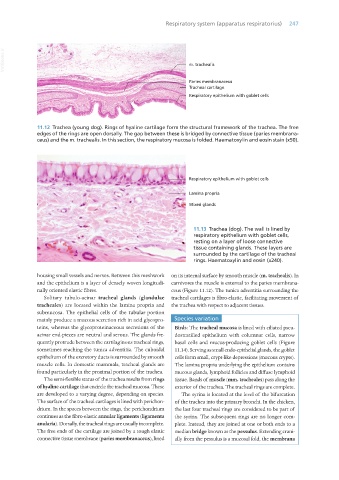
11.12 Trachea (young dog). Rings of hyaline cartilage form the structural framework of the trachea. The free
edges of the rings are open dorsally. The gap between these is bridged by connective tissue (paries membrana-
ceus) and the m. trachealis. In this section, the respiratory mucosa is folded. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x50).
11.13 Trachea (dog). The wall is lined by
respiratory epithelium with goblet cells,
resting on a layer of loose connective
tissue containing glands. These layers are
surrounded by the cartilage of the tracheal
rings. Haematoxylin and eosin (x240).
housing small vessels and nerves. Between this meshwork on its internal surface by smooth muscle (m. trachealis). In
and the epithelium is a layer of densely woven longitudi- carnivores the muscle is external to the paries membrana-
nally oriented elastic fibres. ceus (Figure 11.12). The tunica adventitia surrounding the
Solitary tubulo-acinar tracheal glands (glandulae tracheal cartilages is fibro-elastic, facilitating movement of
tracheales) are located within the lamina propria and the trachea with respect to adjacent tissues.
submucosa. The epithelial cells of the tubular portion
mainly produce a mucous secretion rich in acid glycopro- Species variation
teins, whereas the glycoproteinaceous secretions of the Birds: The tracheal mucosa is lined with ciliated pseu-
acinar end-pieces are neutral and serous. The glands fre- dostratified epithelium with columnar cells, narrow
quently protrude between the cartilaginous tracheal rings, basal cells and mucus-producing goblet cells (Figure
sometimes reaching the tunica adventitia. The cuboidal 11.14). Serving as small endo-epithelial glands, the goblet
epithelium of the excretory ducts is surrounded by smooth cells form small, crypt-like depressions (mucous crypts).
muscle cells. In domestic mammals, tracheal glands are The lamina propria underlying the epithelium contains
found particularly in the proximal portion of the trachea. mucous glands, lymphoid follicles and diffuse lymphoid
The semi-flexible status of the trachea results from rings tissue. Bands of muscle (mm. tracheales) pass along the
of hyaline cartilage that encircle the tracheal mucosa. These exterior of the trachea. The tracheal rings are complete.
are developed to a varying degree, depending on species. The syrinx is located at the level of the bifurcation
The surface of the tracheal cartilages is lined with perichon- of the trachea into the primary bronchi. In the chicken,
drium. In the spaces between the rings, the perichondrium the last four tracheal rings are considered to be part of
continues as the fibro-elastic annular ligaments (ligamenta the syrinx. The subsequent rings are no longer com-
anularia). Dorsally, the tracheal rings are usually incomplete. plete. Instead, they are joined at one or both ends to a
The free ends of the cartilage are joined by a tough elastic median bridge known as the pessulus. Extending crani-
connective tissue membrane (paries membranaceus), lined ally from the pessulus is a mucosal fold, the membrana
Vet Histology.indb 247 16/07/2019 15:03