Page 263 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 263
Respiratory system (apparatus respiratorius) 245
VetBooks.ir
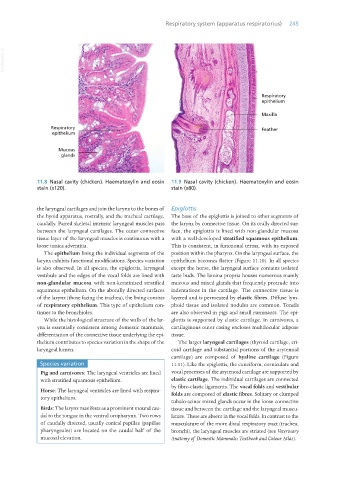
11.8 Nasal cavity (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin 11.9 Nasal cavity (chicken). Haematoxylin and eosin
stain (x120). stain (x80).
the laryngeal cartilages and join the larynx to the bones of Epiglottis
the hyoid apparatus, rostrally, and the tracheal cartilage, The base of the epiglottis is joined to other segments of
caudally. Paired skeletal intrinsic laryngeal muscles pass the larynx by connective tissue. On its orally directed sur-
between the laryngeal cartilages. The outer connective face, the epiglottis is lined with non-glandular mucosa
tissue layer of the laryngeal muscles is continuous with a with a well-developed stratified squamous epithelium.
loose tunica adventitia. This is consistent, in functional terms, with its exposed
The epithelium lining the individual segments of the position within the pharynx. On the laryngeal surface, the
larynx exhibits functional modifications. Species variation epithelium becomes flatter (Figure 11.10). In all species
is also observed. In all species, the epiglottis, laryngeal except the horse, the laryngeal surface contains isolated
vestibule and the edges of the vocal folds are lined with taste buds. The lamina propria houses numerous mainly
non-glandular mucosa with non-keratinised stratified mucous and mixed glands that frequently protrude into
squamous epithelium. On the aborally directed surfaces indentations in the cartilage. The connective tissue is
of the larynx (those facing the trachea), the lining consists layered and is permeated by elastic fibres. Diffuse lym-
of respiratory epithelium. This type of epithelium con- phoid tissue and isolated nodules are common. Tonsils
tinues to the bronchioles. are also observed in pigs and small ruminants. The epi-
While the histological structure of the walls of the lar- glottis is supported by elastic cartilage. In carnivores, a
ynx is essentially consistent among domestic mammals, cartilaginous outer casing encloses multilocular adipose
differentiation of the connective tissue underlying the epi- tissue.
thelium contributes to species variation in the shape of the The larger laryngeal cartilages (thyroid cartilage, cri-
laryngeal lumen. coid cartilage and substantial portions of the arytenoid
cartilage) are composed of hyaline cartilage (Figure
Species variation 11.11). Like the epiglottis, the cuneiform, corniculate and
Pig and carnivores: The laryngeal ventricles are lined vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilage are supported by
with stratified squamous epithelium. elastic cartilage. The individual cartilages are connected
by fibro-elastic ligaments. The vocal folds and vestibular
Horse: The laryngeal ventricles are lined with respira-
tory epithelium. folds are composed of elastic fibres. Solitary or clumped
tubulo-acinar mixed glands occur in the loose connective
Birds: The larynx manifests as a prominent mound cau- tissue and between the cartilage and the laryngeal muscu-
dal to the tongue in the ventral oropharynx. Two rows lature. These are absent in the vocal folds. In contrast to the
of caudally directed, usually conical papillae (papillae musculature of the more distal respiratory tract (trachea,
pharyngeales) are located on the caudal half of the bronchi), the laryngeal muscles are striated (see Veterinary
mucosal elevation. Anatomy of Domestic Mammals: Textbook and Colour Atlas).
Vet Histology.indb 245 16/07/2019 15:02