Page 110 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 110
94 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
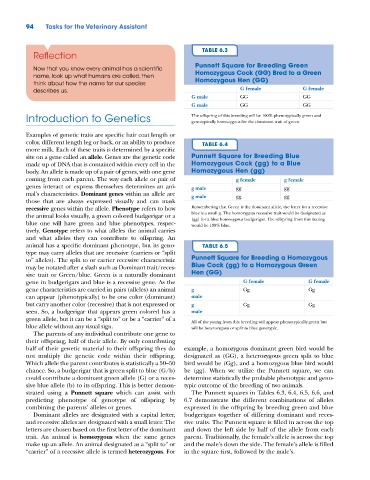
TABLE 6.3
Reflection
Punnett Square for Breeding Green
Now that you know every animal has a scientific
name, look up what humans are called, then Homozygous Cock (GG) Bred to a Green
think about how the name for our species Homozygous Hen (GG)
describes us. G female G female
G male GG GG
G male GG GG
Introduction to Genetics The offspring of this breeding will be 100% phenotypically green and
genotypically homozygous for the dominant trait of green.
Examples of genetic traits are specific hair coat length or
color, different length leg or back, or an ability to produce TABLE 6.4
more milk. Each of these traits is determined by a specific
site on a gene called an allele. Genes are the genetic code Punnett Square for Breeding Blue
made up of DNA that is contained within every cell in the Homozygous Cock (gg) to a Blue
body. An allele is made up of a pair of genes, with one gene Homozygous Hen (gg)
coming from each parent. The way each allele or pair of g female g female
genes interact or express themselves determines an ani- g male gg gg
mal’s characteristics. Dominant genes within an allele are g male gg gg
those that are always expressed visually and can mask
recessive genes within the allele. Phenotype refers to how Remembering that Green is the dominant allele, the letter for a recessive
the animal looks visually, a green colored budgerigar or a blue is a small g. The homozygous recessive trait would be designated as
(gg) for a blue homozygous budgerigar. The offspring from this mating
blue one will have green and blue phenotypes, respec- would be 100% blue.
tively. Genotype refers to what alleles the animal carries
and what alleles they can contribute to offspring. An
animal has a specific dominant phenotype, but its geno- TABLE 6.5
type may carry alleles that are recessive (carriers or “split
to” alleles). The split to or carrier recessive characteristic Punnett Square for Breeding a Homozygous
may be notated after a slash such as Dominant trait/reces- Blue Cock (gg) to a Homozygous Green
sive trait or Green/blue. Green is a naturally dominant Hen (GG)
gene in budgerigars and blue is a recessive gene. As the G female G female
gene characteristics are carried in pairs (alleles) an animal g Gg Gg
can appear (phenotypically) to be one color (dominant) male
but carry another color (recessive) that is not expressed or g Gg Gg
seen. So, a budgerigar that appears green colored has a male
green allele, but it can be a “split to” or be a “carrier” of a All of the young from this breeding will appear phenotypically green but
blue allele without any visual sign. will be heterozygous or split to blue genotypic.
The parents of any individual contribute one gene to
their offspring, half of their allele. By only contributing
half of their genetic material to their offspring they do example, a homozygous dominant green bird would be
not multiply the genetic code within their offspring. designated as (GG), a heterozygous green split to blue
Which allele the parent contributes is statistically a 50–50 bird would be (Gg), and a homozygous blue bird would
chance. So, a budgerigar that is green split to blue (G/b) be (gg). When we utilize the Punnett square, we can
could contribute a dominant green allele (G) or a reces- determine statistically the probable phenotypic and geno-
sive blue allele (b) to its offspring. This is better demon- typic outcome of the breeding of two animals.
strated using a Punnett square which can assist with The Punnett squares in Tables 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, and
predicting phenotype of genotype of offspring by 6.7 demonstrate the different combinations of alleles
combining the parents’ alleles or genes. expressed in the offspring by breeding green and blue
Dominant alleles are designated with a capital letter, budgerigars together of differing dominant and reces-
and recessive alleles are designated with a small letter. The sive traits. The Punnett square is filled in across the top
letters are chosen based on the first letter of the dominant and down the left side by half of the allele from each
trait. An animal is homozygous when the same genes parent. Traditionally, the female’s allele is across the top
make up an allele. An animal designated as a “split to” or and the male’s down the side. The female’s allele is filled
“carrier” of a recessive allele is termed heterozygous. For in the square first, followed by the male’s.