Page 131 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 131
Chapter 7 Feeds and Feeding 115
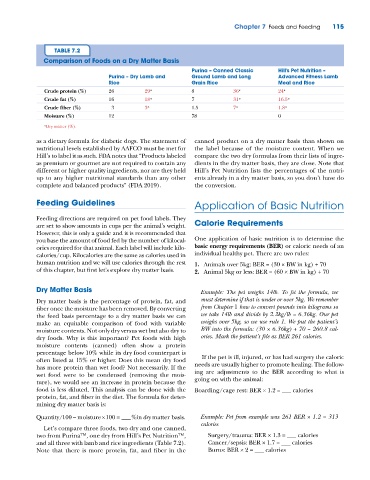
TABLE 7.2
Comparison of Foods on a Dry Matter Basis
Purina – Canned Classic Hill’s Pet Nutrition –
Purina – Dry Lamb and Ground Lamb and Long Advanced Fitness Lamb
Rice Grain Rice Meal and Rice
Crude protein (%) 26 29 a 8 36 a 24 a
Crude fat (%) 16 18 a 7 31 a 16.5 a
Crude fiber (%) 3 3 a 1.5 7 a 1.8 a
Moisture (%) 12 78 0
a Dry matter (%).
as a dietary formula for diabetic dogs. The statement of canned product on a dry matter basis than shown on
nutritional levels established by AAFCO must be met for the label because of the moisture content. When we
Hill’s to label it as such. FDA notes that “Products labeled compare the two dry formulas from their lists of ingre-
as premium or gourmet are not required to contain any dients in the dry matter basis, they are close. Note that
different or higher quality ingredients, nor are they held Hill’s Pet Nutrition lists the percentages of the nutri-
up to any higher nutritional standards than any other ents already in a dry matter basis, so you don’t have do
complete and balanced products” (FDA 2019). the conversion.
Feeding Guidelines Application of Basic Nutrition
Feeding directions are required on pet food labels. They
are set to show amounts in cups per the animal’s weight. Calorie Requirements
However, this is only a guide and it is recommended that
you base the amount of food fed by the number of kilocal- One application of basic nutrition is to determine the
ories required for that animal. Each label will include kilo- basic energy requirements (BER) or caloric needs of an
calories/cup. Kilocalories are the same as calories used in individual healthy pet. There are two rules:
human nutrition and we will use calories through the rest 1. Animals over 5kg: BER = (30 × BW in kg) + 70
of this chapter, but first let’s explore dry matter basis. 2. Animal 5kg or less: BER = (60 × BW in kg) + 70
Dry Matter Basis Example: The pet weighs 14lb. To fit the formula, we
Dry matter basis is the percentage of protein, fat, and must determine if that is under or over 5kg. We remember
fiber once the moisture has been removed. By converting from Chapter 1 how to convert pounds into kilograms so
the feed basis percentage to a dry matter basis we can we take 14lb and divide by 2.2kg/lb = 6.36kg. Our pet
make an equitable comparison of food with variable weighs over 5kg, so we use rule 1. We put the patient’s
moisture contents. Not only dry versus wet but also dry to BW into the formula: (30 × 6.36kg) + 70 = 260.8 cal-
dry foods. Why is this important? Pet foods with high ories. Mark the patient’s file as BER 261 calories.
moisture contents (canned) often show a protein
percentage below 10% while its dry food counterpart is
often listed at 15% or higher. Does this mean dry food If the pet is ill, injured, or has had surgery the caloric
has more protein than wet food? Not necessarily. If the needs are usually higher to promote healing. The follow-
wet food were to be condensed (removing the mois- ing are adjustments to the BER according to what is
ture), we would see an increase in protein because the going on with the animal:
food is less diluted. This analysis can be done with the Boarding/cage rest: BER × 1.2 = ___ calories
protein, fat, and fiber in the diet. The formula for deter-
mining dry matter basis is:
Quantity/100 – moisture 100 ___% in dry matterbasis. Example: Pet from example was 261 BER × 1.2 = 313
calories
Let’s compare three foods, two dry and one canned,
two from Purina™, one dry from Hill’s Pet Nutrition™, Surgery/trauma: BER × 1.3 = ___ calories
and all three with lamb and rice ingredients (Table 7.2). Cancer/sepsis: BER × 1.7 = ___ calories
Note that there is more protein, fat, and fiber in the Burns: BER × 2 = ___ calories