Page 210 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 210
194 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
Right dose: calculate quantity or amount to administer, pinna and lift up and out, which straightens the canal
check the dose with a co‐worker out enough to see it with an otoscope (Figure 11.9a).
Right time/frequency: in which the medications are given You may be asked to restrain the animal for the tech-
on time. nician or veterinarian so use a good sitting restraint with
the animal’s head pressed into your shoulder and a hand
Ear Cleaning and Medicating wrapped around the muzzle. If possible, have the owner
offer treats or cheese on a stick as the cleaning procedure
is started to distract the pet. Try without a muzzle but if
Dogs’ and cats’ ears often require cleaning and some- the ears are too sore or the patient is wanting to bite, go
times medications for bacterial, yeast, or parasite infec- ahead and muzzle the patient.
tions or sores from fly bites, plant awns, or bites from Dirty or infected ears smell bad, almost like stale
other pets. Patients often vigorously shake their heads, beer or yeast. If they do smell bad, have the veterinarian
have a head tilt, or are even off balance because of ear look at them before cleaning. He/she may ask for an
infections. These ears can be sore, and the patient may ear swab before the cleaning to determine if the ears
not tolerate the procedure. If necessary, you will need to are infected with bacteria, yeast, or mites. Supplies
muzzle these patients or the veterinarian may choose to needed include four long applicator sticks, two micro-
administer a sedative. scope slides, one with a drop of mineral oil on it. One
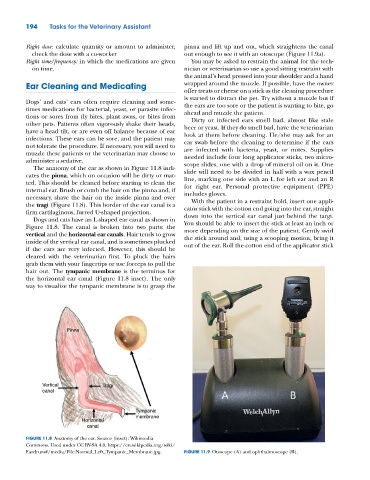
The anatomy of the ear as shown in Figure 11.8 indi-
cates the pinna, which on occasion will be dirty or mat- slide will need to be divided in half with a wax pencil
line, marking one side with an L for left ear and an R
ted. This should be cleaned before starting to clean the for right ear. Personal protective equipment (PPE)
internal ear. Brush or comb the hair on the pinna and, if includes gloves.
necessary, shave the hair on the inside pinna and over With the patient in a restraint hold, insert one appli-
the tragi (Figure 11.8). This border of the ear canal is a cator stick with the cotton end going into the ear, straight
firm cartilaginous, furred U‐shaped projection. down into the vertical ear canal just behind the targi.
Dogs and cats have an L‐shaped ear canal as shown in
Figure 11.8. The canal is broken into two parts: the You should be able to insert the stick at least an inch or
more depending on the size of the patient. Gently swirl
vertical and the horizontal ear canals. Hair tends to grow the stick around and, using a scooping motion, bring it
inside of the vertical ear canal, and is sometimes plucked out of the ear. Roll the cotton end of the applicator stick
if the ears are very infected. However, this should be
cleared with the veterinarian first. To pluck the hairs
grab them with your fingertips or use forceps to pull the
hair out. The tympanic membrane is the terminus for
the horizontal ear canal (Figure 11.8 inset). The only
way to visualize the tympanic membrane is to grasp the
Pinna
Vertical Tragi
canal
Tympanic
membrane
Horizontal
canal
FIGURE 11.8 Anatomy of the ear. Source (inset): Wikimedia
Commons. Used under CC BY‐SA 4.0, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Eardrum#/media/File:Normal_Left_Tympanic_Membrane.jpg. FIGURE 11.9 Otoscope (A) and ophthalmoscope (B).