Page 215 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 215
Goniometry 201
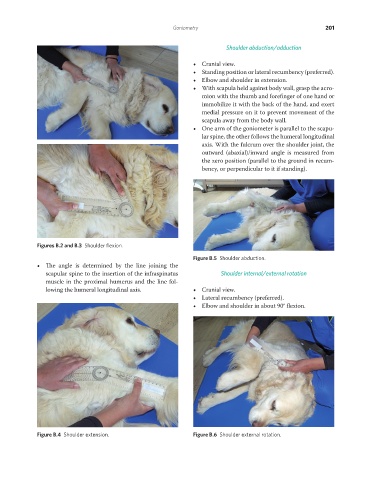
Shoulder abduction/adduction
• Cranial view.
• Standing position or lateral recumbency (preferred).
• Elbow and shoulder in extension.
• With scapula held against body wall, grasp the acro-
mion with the thumb and forefinger of one hand or
immobilize it with the back of the hand, and exert
medial pressure on it to prevent movement of the
scapula away from the body wall.
• One arm of the goniometer is parallel to the scapu-
lar spine, the other follows the humeral longitudinal
axis. With the fulcrum over the shoulder joint, the
outward (abaxial)/inward angle is measured from
the zero position (parallel to the ground in recum-
bency, or perpendicular to it if standing).
Figures B.2 and B.3 Shoulder flexion.
Figure B.5 Shoulder abduction.
• The angle is determined by the line joining the
scapular spine to the insertion of the infraspinatus Shoulder internal/external rotation
muscle in the proximal humerus and the line fol-
lowing the humeral longitudinal axis. • Cranial view.
• Lateral recumbency (preferred).
• Elbow and shoulder in about 90° flexion.
Figure B.4 Shoulder extension. Figure B.6 Shoulder external rotation.
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 201 08/08/2019 09:50