Page 219 - Veterinary Laser Therapy in Small Animal Practice
P. 219
Goniometry 205
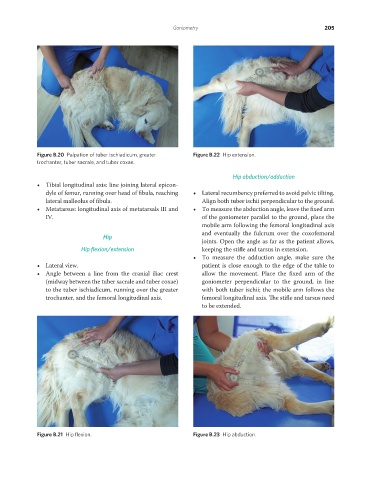
Figure B.20 Palpation of tuber ischiadicum, greater Figure B.22 Hip extension.
trochanter, tuber sacrale, and tuber coxae.
Hip abduction/adduction
• Tibial longitudinal axis: line joining lateral epicon-
dyle of femur, running over head of fibula, reaching • Lateral recumbency preferred to avoid pelvic tilting.
lateral malleolus of fibula. Align both tuber ischii perpendicular to the ground.
• Metatarsus: longitudinal axis of metatarsals III and • To measure the abduction angle, leave the fixed arm
IV. of the goniometer parallel to the ground, place the
mobile arm following the femoral longitudinal axis
Hip and eventually the fulcrum over the coxofemoral
joints. Open the angle as far as the patient allows,
Hip flexion/extension keeping the stifle and tarsus in extension.
• To measure the adduction angle, make sure the
• Lateral view. patient is close enough to the edge of the table to
• Angle between a line from the cranial iliac crest allow the movement. Place the fixed arm of the
(midway between the tuber sacrale and tuber coxae) goniometer perpendicular to the ground, in line
to the tuber ischiadicum, running over the greater with both tuber ischii; the mobile arm follows the
trochanter, and the femoral longitudinal axis. femoral longitudinal axis. The stifle and tarsus need
to be extended.
Figure B.21 Hip flexion. Figure B.23 Hip abduction.
REDONDO PRINT (4-COL BLEED).indd 205 08/08/2019 09:51