Page 21 - MHF-FeedingMinds-final.indd
P. 21
12 1.1 Nutritional Requirements
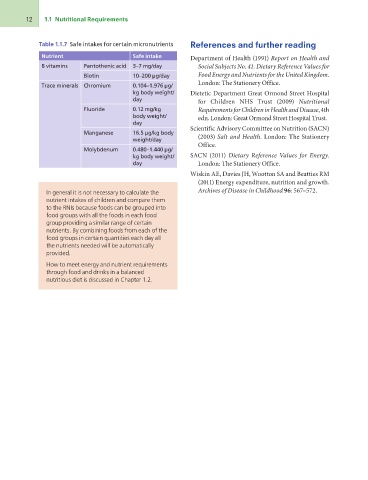
Table 1.1.7 Safe intakes for certain micronutrients References and further reading
Nutrient Pantothenic acid Safe intake Department of Health (1991) Report on Health and
B vitamins Biotin Social Subjects No. 41. Dietary Reference Values for
Chromium 3–7 mg/day Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom.
Trace minerals London: The Stationery Office.
Fluoride 10–200 µg/day
Dietetic Department Great Ormond Street Hospital
Manganese 0.104–1.976 µg/ for Children NHS Trust (2009) Nutritional
Molybdenum kg body weight/ Requirements for Children in Health and Disease, 4th
day edn. London: Great Ormond Street Hospital Trust.
0.12 mg/kg Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN)
body weight/ (2003) Salt and Health. London: The Stationery
day Office.
16.5 µg/kg body SACN (2011) Dietary Reference Values for Energy.
weight/day London: The Stationery Office.
0.480–1.440 µg/ Wiskin AE, Davies JH, Wootton SA and Beatties RM
kg body weight/ (2011) Energy expenditure, nutrition and growth.
day Archives of Disease in Childhood 96: 567–572.
In general it is not necessary to calculate the
nutrient intakes of children and compare them
to the RNIs because foods can be grouped into
food groups with all the foods in each food
group providing a similar range of certain
nutrients. By combining foods from each of the
food groups in certain quantities each day all
the nutrients needed will be automatically
provided.
How to meet energy and nutrient requirements
through food and drinks in a balanced
nutritious diet is discussed in Chapter 1.2.