Page 165 - Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
P. 165
2.12 Chlorpropamide and Other Sulfonylureas
Shown below are the structures of tolbutamide potassium channels.
Tolbutamide
1. It is not uncommon for patients with type 2 diabetes ate that a drug interaction could occur?
Losartan Chlorpropamide
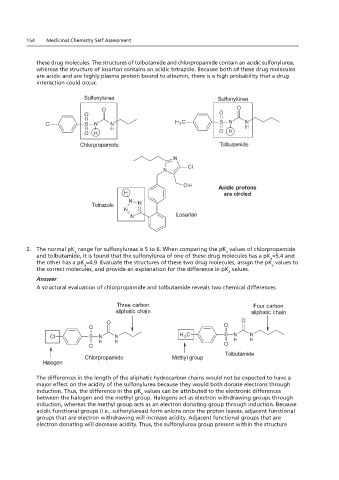
154 Medicinal Chemistry Self Assessment
these drug molecules. The structures of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide contain an acidic sulfonylurea,
Answer
whereas the structure of losartan contains an acidic tetrazole. Because both of these drug molecules
are acidic and are highly plasma protein bound to albumin, there is a high probability that a drug
Plasma protein binding interactions (also known as that a drug interaction could occur.
interaction could occur.
Sulfonylurea Sulfonylurea
Chlorpropamide Tolbutamide
Acidic protons
are circled
Tetrazole
Losartan
2. The normal pK range for sulfonylureas is 5 to 6. When comparing the pK values of chlorpropamide
a
a
and tolbutamide, it is found that the sulfonylurea of one of these drug molecules has a pK =5.4 and
a
the other has a pK =4.9. Evaluate the structures of these two drug molecules, assign the pK values to
a
a
the correct molecules, and provide an explanation for the difference in pK values.
a
2. The normal pK a range forrect molecules, and provide an explanation for the difference in pKa values.
Answer
Answer
A structural evaluation of chlorpropamide and tolbutamide reveals two chemical differences.
Three carbon Four carbon
aliphatic chain aliphatic chain
Tolbutamide
Chlorpropamide Methyl group
Halogen
The differences in the length of the aliphatic hydrocarbon chains would not be expected to have a
major effect on the acidity of the sulfonylurea because they would both donate electrons through
3. Using your answer from question 2, that will be ionized at an intestinal pH of 6.1.
induction. Thus, the difference in the pK values can be attributed to the electronic differences
a
between the halogen and the methyl group. Halogens act as electron withdrawing groups through
Answer
induction, whereas the methyl group acts as an electron donating group through induction. Because
acidic functional groups (i.e., sulfonylureas) form anions once the proton leaves, adjacent functional
groups that are electron withdrawing will increase acidity. Adjacent functional groups that are
[Base~Form]
electron donating will decrease acidity. Thus, the sulfonylurea group present within the structure
pH=~pK +log ~
a
[Acid~Form]
[Base~Form]
6.1=~5.4+log ~
[Acid~Form]
[Base~Form]
0.7 =~log ~
[Acid~Form]
>Base~Form @ 5.01 >Base~Form @
5.01=~ ~or~ =~
> @Acid~Form 1 > @Acid~Form
This ratio indicates that for every one molecule group in the acid (or unionized) that are unionized.
5.01~molecules~in~base~form~+~1.0~molecule~in~acid~form~=~6.01~total~molecules
Base~form=Ionized~form~and~Acid~form=Unionized~form
5.01~Molecules~in~Ionized~Form
Percent~in~Ionized~Form= ×100%=83.4%
6.01~Total~Molecules
1~Molecule~in~Unionized~Form
Percent~in~Unionized~Form= ×100%=16.6%
6.01~Total~Molecules